Crab meat vs. Lobster - What is the difference?


Summary
Crab meat has a sweeter, more delicate flavor than lobster, with a more robust, savory taste. Crab meat is generally more tender and flakier than lobster meat, which can be firmer and denser.
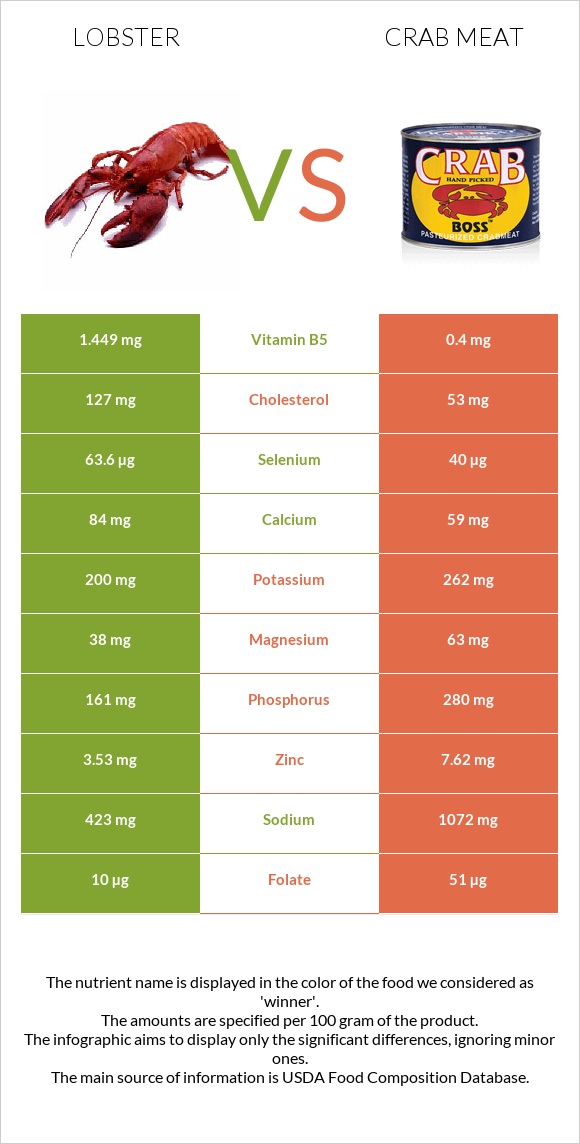
Crab meat is the winner in the vitamin category, being eight times richer in vitamin B12, seven times richer in vitamin A, and five times richer in folate or vitamin B9. However, lobster is four times richer in vitamin B5. Crab is about three times lower in cholesterol.
While lobster is a better source of selenium, manganese, and calcium, crab meat is higher in iron, zinc, and phosphorus. Lobster is lower in sodium.
Introduction
Crab meat and lobster are both types of shellfish that are popular in many cuisines around the world. In this article, we will look at these two foods' nutrition and health impacts and find out the differences between them.
Are crab meat and lobster the same?
Classification and Appearance
Crabs and lobsters are both classified as members of the phylum Arthropoda and the subphylum Crustacea. However, they belong to different families within the order Decapoda, which includes other crustaceans such as shrimp, prawns, and crayfish.
Crabs are classified in the family Portunidae, which includes over 400 species of crabs found in both saltwater and freshwater habitats worldwide.
Lobsters, conversely, are classified in the family Nephropidae, which includes over 50 species of lobsters found in cold, deep waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
Crabs have a broad, flattened body and typically have five pairs of legs, with the first pair modified into claws. Lobsters have long, cylindrical bodies with five pairs of legs, the first two modified into large claws.
In summary, we can surely say that crab meat and lobster are not the same thing.
Taste and Use
Crab meat has a sweeter, more delicate flavor than lobster, which has a stronger, more savory taste. Crab meat is generally more tender and flakier than lobster meat, which can be firmer and denser.
Both crab meat and lobster can be prepared in various ways, such as boiled, steamed, grilled, or baked, but they may require different cooking times and methods.
Nutrition
The information below is presented for 100g servings of Alaskan king crab and northern lobster, both cooked with moist heat.
The average serving size per person for these foods is considered 3 ounces or 85g.
Macronutrients and Calories
The two types of seafood have nearly identical macronutrient compositions, consisting of 78% water, 19% protein, and only 3% other nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+30.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+79.1%
Calories
Crab meat and lobster are medium-calorie foods.
Crab meat is only slightly higher in calories, eight calories per 100g, to be precise. In a 100g serving, crab meat provides 97 calories, compared to the 89 calories of lobster.
Protein
These two foods provide essentially the same amount of protein, with crab meat having only 0.35g more per 100g serving.
Lobster and crab meat fall in the top 27% of foods as a source of protein, containing 19g of this nutrient in a 100g serving. This covers 45% of the daily needed protein value.
Crab and lobster contain high levels of all essential amino acids. Crab meat is slightly higher in all of these except for histidine.
Fats
While crab meat is two times higher in fats, these two dishes are very low-fat foods, providing less than 2g per 100g serving.
Crab meat has a preferable fat profile, being richer in polyunsaturated fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, and lower in saturated fats. Crab meat is also almost three times lower in cholesterol.
Despite being low in fats, these two types of seafood, especially lobster, are high in cholesterol. Lobster falls in the top 7% of foods as a source of cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+36.8%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-36.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+57.6%
Carbohydrates
Like most other seafood and meat in general, lobster and crab meat do not contain carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Crab meat is the ultimate winner in the vitamin category, being eight times richer in vitamin B12, seven times richer in vitamin A, five times richer in folate or vitamin B9, and three times richer in vitamin B2. Crab meat is also higher in vitamins C, B1, and B6.
Nevertheless, lobster contains four times more vitamin B5 and 1.4 times more vitamin B3.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+36.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+316.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+800%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+130.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+223.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+51.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+704.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+363.6%
Minerals
Crab meat can also be a better source of many minerals. It contains higher levels of iron, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium.
However, lobster is richer in selenium, manganese, calcium, and copper. Lobster is also lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+62.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+31.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-54.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+62.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+82.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+46.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+162.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+88.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+51.4%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, such as crab meat and lobster, is considered to be 0, as these foods do not increase blood glucose levels after consumption.
Health Impact
Seafood is known for being an excellent healthy source of protein, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals. Shellfish, such as crab meat and lobster, are no exception.
In this section, we will look at some scientific findings about the health impacts of crab meat and lobster. Of course, there are some differences in the health impacts these two foods provide. However, crab meat and lobsters share a lot of health benefits as they belong to the same group mentioned above.
Cardiovascular Health
Research focusing on omega-3 fatty acid intake has concluded that 1 to 2 seafood meals per week should be consumed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke, and sudden cardiac death, especially when seafood replaces the intake of less healthy foods (1). Crab meat is a better source of omega-3 fatty acids compared to lobster.
Studies also find that substituting seafood for other dietary animal products may be cardioprotective, whether or not they are high in n-3 fatty acids, due to the lower level of saturated fats and cholesterol (2). While crab and lobster are higher in cholesterol than most other seafood products, crab meat contains less cholesterol.
That being said, it’s essential to mention the words of Eric Rimm, professor in the Departments of Epidemiology and Nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (3):
“Dietary cholesterol isn’t as important as was once thought. In the context of an overall healthy diet, dietary cholesterol is not strongly related to an increase in blood cholesterol or heart disease.”
Diabetes
As mentioned above, crab meat and lobster contain no carbohydrates, thus having glycemic index values of 0. This means that consuming these foods does not raise blood glucose levels but still affects blood insulin levels.
Studies find that eating a lot of seafood can reduce both fasting and postprandial risk markers of insulin resistance. However, the exception is shellfish, such as lobster and crab, and fried lean fish, the intake of which is associated with impaired glycaemic control (4).
At the same time, crab meat and lobster are rich in a phytochemical called astaxanthin. This phytochemical has been researched to improve insulin resistance and secretion, reduce hyperglycemia, and have protective effects against retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy (5).
Brain health
Some studies show that B-complex vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids amplify each other's function and may enhance cognitive functioning (6). Crab meat and lobster are extremely rich in these nutrients. Hence, consumption of these foods may be beneficial for brain health.
Allergy
Crab meat and lobster are included in the list of top food allergens in the US (7). Symptoms of this allergy may include diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps and pain, shortness of breath, and swelling of the throat. There may be phases of anaphylactic shock that require immediate treatment (8).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6903778/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705336/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/lobster-healthy-protein/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6536831/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7401277/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25877495/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4241964/
- https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/food/shellfish/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.43µg | 11.5µg | 420% |
| Selenium | 73.1µg | 40µg | 60% |
| Copper | 1.55mg | 1.182mg | 41% |
| Zinc | 4.05mg | 7.62mg | 32% |
| Cholesterol | 146mg | 53mg | 31% |
| Sodium | 486mg | 1072mg | 25% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.667mg | 0.4mg | 25% |
| Choline | 80.9mg | 15% | |
| Phosphorus | 185mg | 280mg | 14% |
| Folate | 11µg | 51µg | 10% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 7.6mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1mg | 7% | |
| Iron | 0.29mg | 0.76mg | 6% |
| Magnesium | 43mg | 63mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.119mg | 0.18mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 96mg | 59mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.053mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.017mg | 0.055mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.83mg | 1.34mg | 3% |
| Protein | 19g | 19.35g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.86g | 1.54g | 1% |
| Potassium | 230mg | 262mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.065mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.34g | 0.536g | 1% |
| Calories | 89kcal | 97kcal | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 1 IU | 0% | |
| Trans fat | 0.013g | N/A | |
| Saturated fat | 0.208g | 0.133g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.253g | 0.185g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.248mg | 0.269mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.753mg | 0.783mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.832mg | 0.938mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.376mg | 1.536mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.426mg | 1.684mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.475mg | 0.545mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.782mg | 0.817mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.852mg | 0.91mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.475mg | 0.393mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.117g | 0.295g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.078g | 0.118g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.05g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | 0.031g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.033g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lobster - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174209/nutrients
- Crab meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174202/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





