Mussels vs. Oysters — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Mussels are over 2 times richer in protein. They are also somewhat higher in calories, fats, and carbohydrates.
Mussels are the absolute winner in the vitamin category, being richer in all of them.
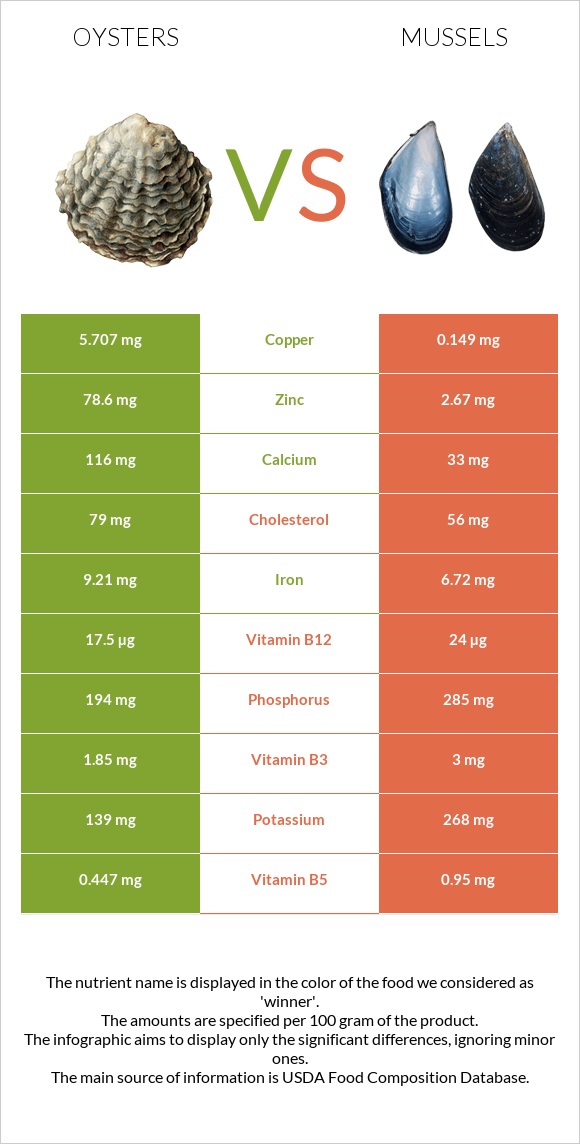
Oysters are 38 times richer in copper and 29 times richer in zinc. However, mussels contain 11 times more manganese and 2 times more selenium.
Introduction
Mussels and oysters are two different types of seafood. While people often confuse the two, and though both are bivalves, certain qualities set them apart.
This article will compare mussels and oysters according to their general use, nutritional content, and health impacts.
Habitat
Mussel is seafood that can come from freshwater or saltwater source. On the other hand, the oyster is a seafood that only comes from saltwater sources.
The natural habitat of saltwater mussels is the ocean. It is the most commonly consumed type of mussel worldwide. Freshwater mussels are mostly considered inedible. However, throughout history, some Native American tribes used freshwater mussels as vital sources of nutrients.
Oysters are highly available in rocky sea basins, and for centuries, oysters have been considered both a luxurious food and food for the working class. This is due to its availability in certain regions and ease of gathering. In addition to gastronomy, oysters function as natural water filtration and are natural indicators for pollution.
There are different types of mussels; the most common edible ones are usually farm-raised blue mussels and green mussels.
Culinary Use
Mussels and oysters can be very versatile when it comes to their methods of preparation. In different parts of the world, they are prepared and consumed differently. These bivalve mollusks can be consumed raw or cooked.
Like any seafood, mussels and oysters are best when they are fresh. However, unlike most seafood, if they are not alive when prepared or cooked, eating them could result in food poisoning since the enzymes in them break down the tissues, producing poisonous components.
Mussels can be fried, smoked, roasted, and grilled with different types of oil. Mussels have a distinctive sweet and salty flavor. They are often described as having a similar taste to clams; however, with a more robust and pronounced taste. The meat is tender, slightly chewy, and has a rich, buttery texture.
In France, Belgium, and the Netherlands, mussels are accompanied by fries, and this famous dish is called “Moules et Frites.” In Italy, a famous mussel dish is made with white wine sauce. The mussels are steam-cooked with herbs, garlic, and white wine.
Oysters were part of the culinary culture of many civilizations that lived on the shorelines. Eating an oyster can range from the simplest methods – cutting it open and eating it – to more complex dishes, such as the oyster Rockefeller. This is a famous oyster dish created in New Orleans. Other popular methods of serving oysters are raw with a squeeze of lemon, fried, grilled, or smoked.
Nutritional Content
In this section of the article, we will compare 100g servings of mussels and oysters, both cooked in moist heat.
However, an average serving of these foods per person is considered 3 ounces, equal to 85g.
Calories
Mussels provide 1.7 times more calories than oysters, containing 172 calories per 100g, while the same serving of oysters has 102 calories.
Proteins
Mussels are over 2 times richer in protein compared to oysters. Overall, a 100g serving of mussels covers 57% of the required daily value of proteins, while this number for oysters is 27%.
A 100g serving of mussels and oysters contains 23.4g and 11.4g of protein, respectively.
As expected, mussels are richer in all of the essential amino acids. Oysters are low in threonine, and they are both relatively low in methionine, valine, and phenylalanine.
Fats
While mussels are relatively higher in fats than oysters, these two foods are not high in fats. A 100g serving of mussels contains 1g more fats, providing 4.5g, whereas the same serving of oysters has 3.4g of fats.
Mussels have a more favorable fat profile, as they are richer in unsaturated fats and somewhat lower in saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-10.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+100.4%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+14.8%
Mussels are nearly 2 times higher in omega-3 DHA and DPA, while oysters are richer in omega-3 EPA.
Cholesterol
Despite being higher in fats, mussels are lower in cholesterol, containing 56mg per 100g, while oysters have 79mg.
Both oysters and mussels are high-cholesterol foods. Oysters fall in the top 22% of foods as a source of cholesterol.
Carbs
While these two foods are not particularly high in carbohydrates, mussels are higher in this macronutrient.
A 100g serving of mussels and oysters provides 7.4 and 5.5g of carbohydrates, respectively.
The carb content of mussels and oysters is completely made up of net carbs, as these foods do not contain dietary fiber.
Minerals
Mussels and oysters are rich sources of minerals, providing these micronutrients in varying amounts.
Oysters are 38 times richer in copper and 29 times richer in zinc. They are also richer in calcium and iron and contain less sodium.
On the other hand, mussels contain 11 times more manganese and 2 times more selenium. Potassium and phosphorus levels are also higher in mussels.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+251.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+37.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+3730.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+2843.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-55%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+92.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+46.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1050.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+126.8%
To put these numbers in context, a 100g serving of oysters covers the daily needed value of zinc and copper by 715% and 634%, respectively.
A 100g serving of mussels covers 296% of the daily required value of manganese and 163% of selenium.
Vitamins
Mussels are the absolute winner in this category, being richer in all vitamins. They are excellent sources of most B-group vitamins, covering 1000% of the daily needed value of vitamin B12.
Mussels are 8 times richer in vitamin B1, 5 times richer in folate or vitamin B9, 3 times richer in vitamin A, and 2 times richer in vitamins B2 and B5. They also contain higher levels of vitamins B5, B6, B12, and C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+250%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+733.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+62.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+112.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+63.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+37.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+442.9%
Weight Loss and Diets
Both mussels and oysters can be consumed in the keto diet as they are packed with protein, minerals, and vitamins. However, they should be consumed in moderation as they provide 5 to 7g of carbohydrates per 100g serving.
For overall weight loss, oysters and mussels can be consumed within limits. While these two types of seafood are an excellent source of many nutrients, they are medium-calorie foods and are high in cholesterol.
Health Impacts
Cardiovascular Health
One study found that oyster and mussel intake decreases cholesterol levels in the blood, which is important for preventing atherosclerosis and reducing cardiovascular risk (1, 2).
Mussels and oysters are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to have cardioprotective functions. Omega-3 fatty acids can have a beneficial effect on decreasing the risk of cardiac arrhythmias (3).
Including shellfish like mussels or oysters in a balanced diet can be a heart-healthy choice, offering essential nutrients and potential protection against cardiovascular disease.
Allergies
Shellfish allergies are one of the most common allergies in the world. People allergic to oysters are often also allergic to mussels and vice-versa. This allergic reaction is usually towards a protein found in these mollusks called tropomyosin (4).
Some people with mussel allergies are not allergic to oysters. This type of allergy is caused by a protein found in mussels called paramyosin (4).
Poisoning and Intoxication
Several microalgae species have the ability to produce poisons that reach us through the food we eat. Paralytic shellfish poisoning is caused by consuming contaminated shellfish, including oysters and mussels. It’s known for its unique acute neurological symptoms and even fatal outcomes. Signs of paralytic shellfish poisoning might range from mild tingling or numbness to total respiratory paralysis. In fatal situations, respiratory paralysis happens 2–12 hours after eating contaminated food. Paralytic shellfish poisoning is caused by harmful algal blooms found in the shellfish (5).
Another concern for consumers is bacterial contamination. Eating raw oysters and mussels can be particularly dangerous for people at high risk, such as those with diabetes, liver illness, or weakened immune systems (6). The bacteria that often causes oyster poisoning is from the Vibrio family (7).
Thus, both oysters and mussels need to be handled properly. Freshness, refrigeration, and contamination are the main criteria to be careful of.
Diabetes and Gout
A study focused on the relation of shellfish, such as oysters and mussels, to diabetes and gout. This research concluded that while oysters and mussels may not increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, they might increase uric acid excretion, thus raising gout risk due to a high content of purines (8).
Heavy Metal Contamination
Mussels contain higher levels of mercury, while oysters are considerably higher in cadmium. However, research finds that the average levels of cadmium, mercury, and copper detected in mollusks from the Italian coastline are low, and even when higher shellfish portions are consumed, exposure to these metals is moderate (9).
Anemia
Vitamin B12, folate, and iron deficiency are the leading causes of anemia (10). Thus, consuming foods rich in vitamin B12, folate, and iron can reduce the risk of developing anemia. Mussels are a better source of B-group vitamins; however, oysters are somewhat richer in iron.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19631050/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2349916/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1780156/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24870065/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32550574/
- https://hal.science/hal-02443363/document
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26038900/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33527847/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7700650/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3736489/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Zinc | 78.6mg | 2.67mg | 690% |
| Copper | 5.707mg | 0.149mg | 618% |
| Vitamin B12 | 17.5µg | 24µg | 271% |
| Manganese | 0.591mg | 6.8mg | 270% |
| Selenium | 39.5µg | 89.6µg | 91% |
| Iron | 9.21mg | 6.72mg | 31% |
| Protein | 11.42g | 23.8g | 25% |
| Choline | 130mg | 24% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.036mg | 0.3mg | 22% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.18mg | 0.42mg | 18% |
| Folate | 14µg | 76µg | 16% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 13.6mg | 15% |
| Phosphorus | 194mg | 285mg | 13% |
| Vitamin E | 1.7mg | 11% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.447mg | 0.95mg | 10% |
| Sodium | 166mg | 369mg | 9% |
| Cholesterol | 79mg | 56mg | 8% |
| Calcium | 116mg | 33mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 26µg | 91µg | 7% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.85mg | 3mg | 7% |
| Calories | 102kcal | 172kcal | 4% |
| Potassium | 139mg | 268mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.061mg | 0.1mg | 3% |
| Fats | 3.42g | 4.48g | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2µg | 2% | |
| Carbs | 5.45g | 7.39g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.506g | 1.014g | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.056g | 1.212g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 5.45g | 7.39g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 0% | |
| Magnesium | 35mg | 37mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.23g | N/A | |
| Starch | 0.9g | 0% | |
| Trans fat | 0.068g | N/A | |
| Saturated fat | 0.948g | 0.85g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.138mg | 0.267mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.046mg | 1.025mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.459mg | 1.036mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.716mg | 1.676mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.762mg | 1.779mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.257mg | 0.537mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.413mg | 0.853mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.523mg | 1.04mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.22mg | 0.457mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.353g | 0.276g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.271g | 0.506g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.163g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.02g | 0.044g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.061g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +27.9% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +108.4% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +31% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +35.6% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +109.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Oysters - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171980/nutrients
- Mussels - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174217/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.