Peanut butter vs. Cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cheese is higher in saturated fats and sodium. It is richer in zinc, phosphorus, and calcium vitamins B2, B12, D, and A. Peanut butter is higher in calories and carbs, richer in unsaturated fats, magnesium, iron, copper, and vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, E, and folate.
Peanut butter is a healthier food in this comparison since it is lower in saturated fats and salts. Foods high in salts and saturated fats increase the risks of atherosclerosis and hypertension, increasing overall risks of cardiovascular diseases.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- General differences
- Nutritional content comparison
- Health impacts
- Cardiovascular health
- Positive impacts of cheese on overall health
- Negative impacts of cheese on overall health
- Positive impacts of peanut butter on overall health
- Negative impacts of peanut butter on overall health
- Which is healthier when taking into consideration the health impacts?
- References
Introduction
Cheese is one of the most consumed foods throughout the world. It is suitable for vegetarians, and some cheese can be consumed by people who follow the keto diet. Various cheeses will be discussed in the paragraphs below.
On the other hand, peanut butter is a processed form of peanut nuts and is turned into spreads. Peanut butter available in the market often contains additives, preservatives, and palm oil. They are highly nutritious and provide good macronutrients.
This article will discuss the difference between cheese and peanut butter, considering their general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Their general difference is based on types and shelf life.
Types
Cheese is one of the most versatile foods around the world. Various cheeses are specific to each region, each type of climate, animal-specific, and preparation methods.
We can have cheese from cow, sheep, goat, even vegan sources, most commonly tofu cheese.
There are several types of cheese:
The list of cheeses can go long.
These cheeses are different in their preparation methods, fermentation, types of milk and animal used to make the cheese, the texture of the cheese, culinary usage.
It is essential to understand the differences between these cheeses and use them correctly in the culinary world. We know that using the wrong type of cheese in any Italian food would ruin the dish.
On the other hand, we have peanut butter which is a spread. Types differ between crunchy and smooth creamy. However, it is the same peanut butter.
Shelf life
Peanut butter has a longer shelf life compared to any cheese.
Cheese needs refrigeration. The shelf life of most cheeses is usually up to 10 days in refrigerated forms. Peanut butter available in the market usually has around one year of shelf life.
Nutritional content comparison
Calories
Peanut butter is higher in calories compared to cheese.
Carbs
Peanut butter contains 7 times higher carbs than cheese.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of cheese is 0, whereas the glycemic index of peanut butter is 14, which is considered a low glycemic index.
Proteins
They have nearly similar amounts of proteins.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+54.2%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+622%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+2909.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+28.4%
Fats
Peanut butter contains higher amounts of fats than cheese. They are both high in fats.
It is important to note that the ratio of saturated to unsaturated fats in cheese is higher than in peanut butter. The fat in peanut butter is distributed as monounsaturated fats mainly.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-45.3%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+180.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+782.1%
Minerals
Cheese is richer in zinc, phosphorus, and calcium. However, cheese contains high amounts of sodium that should be considered. On the other hand, peanut butter is richer in magnesium, iron, and copper.
The chart below displays the mineral distribution of cheese and peanut butter.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+522.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+634.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1142.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+1306.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-97.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+6066.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1349%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+45%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+35.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+595.1%
Vitamins
Cheese is richer in vitamins B2, B12, D, and A. whereas peanut butter are richer in vitamin B1, B3, B5, B6, E, and folate.
The chart below displays the vitamin distribution of cheese and peanut butter.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1181.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+417.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+22123.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+177.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+568.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+222.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+122.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+700%
Health impacts
Cheese has negative and positive impacts on overall health. Below, we will be discussing these effects.
Cardiovascular health
Cheese contains some peptides that inhibit ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme), like ACE-inhibitor medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, etc.), so it may decrease blood pressure (1,2). This effect is unknown for peanut butter.
It should be noted that people who take MAO inhibitors (especially antidepressants) may experience a hypertensive crisis when eating cheese due to tyramine (3).
The different types of cheese have different effects on the cholesterol level in the blood (27% fat Gouda-type cheese doesn’t increase the cholesterol level in the blood; the amount of cholesterol in Mozzarella cheese considerably increased over the course of storage, etc.) (4.5).
When consumed in moderation, various types of peanuts result in a less atherogenic lipid profile in hyperlipidaemic individuals (6).
Positive impacts of cheese on overall health
Different types of cheese exist, and each has a slightly different nutritional profile.
Reducing risks of osteoporosis
Since they are rich in calcium, most cheeses provide protective effects from osteoporosis. They maintain healthy bone health. (7) (8)
Digestive system
Cheeses like mozzarella and Parmigiano Reggiano contain Lactobacillus bacteria that have probiotic effects, beneficially affecting the host’s microbiota. They may reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system. (9) (10) (11)
A certain amount of cheese can cause bloating, flatulence, cramps, and diarrhea in lactose-intolerant people.
Cancer
Consumption of calcium-rich foods reduces the risk of colorectal cancer. (13)
Negative impacts of cheese on overall health
Since cheese contains lactose, lactose intolerant people will have nausea, bloating, and diarrhea.
High-sodium cheeses increase the risks of developing hypertension and kidney diseases. (14)
We mentioned above that calcium-rich foods decrease the risk of colorectal cancer; however, it is not the case for prostate cancer. There is an increase in developing prostate cancer with high calcium consumption. (15)
Positive impacts of peanut butter on overall health
Peanut butter is rich in proteins, minerals, vitamins, and healthy fats. Overall, it is an excellent addition to any diet.
Antioxidants
Peanut butter contains antioxidants that reduce chronic inflammation, specifically in rheumatoid arthritis. (16) (17)
Peanut butter contains an antioxidant called resveratrol, decreasing cardiovascular diseases and cancer risks. (18)
Negative impacts of peanut butter on overall health
Peanut butter can trigger an anaphylactic shock in people who have a peanut allergy. In addition, aflatoxins can be present in peanuts that are not processed yet, which is linked with increased liver cancer risks. However, processing removes these peanuts that have gone bad in mass manufacturing. (18)
Peanut butter contains phytic acid, which impairs the absorption of certain nutrients, mostly minerals. (19)
Which is healthier when taking into consideration the health impacts?
The two main concerns regarding both these foods are the additive compounds. When it comes to cheese, it is essential to consider low-salt cheeses as salt contributes to increased risks of hypertension.
It is always advised not to buy peanut butter containing hydrogenated vegetable oils such as palm oil.
Take into consideration the amount of fat and its type present in both these foods.
Cheese is lower in fats; however, it's higher in saturated fats. Peanut butter is higher in total fats, primarily unsaturated. We can consider peanut butter, devoid of hydrogenated oils, healthier as saturated fats increase LDL levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. (20)
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Micloth-Lopez-Del-Castillo/publication/319668728_ACEI_and_antioxidant_peptides_release_during_ripening_of_Mexican_Cotija_hard_cheese/links/59d119524585150177f3cd75/ACEI-and-antioxidant-peptides-release-during-ripening-of-Mexican-Cotija-hard-cheese.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996912001494
- https://europepmc.org/article/med/3283290
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.3402/fnr.v59.27651
- https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20113003205
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/effects-of-peanut-processing-on-body-weight-and-fasting-plasma-lipids/99759C1CB14EA8F648834CAEBA0A6A05
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33237064/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3796667/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3279064/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20838859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21477383/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18096922/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12869397/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30402970/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16522915/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28742266/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24345046/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30696374/
- https://ifst.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-2621.2002.00618.x
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459188/
Infographic
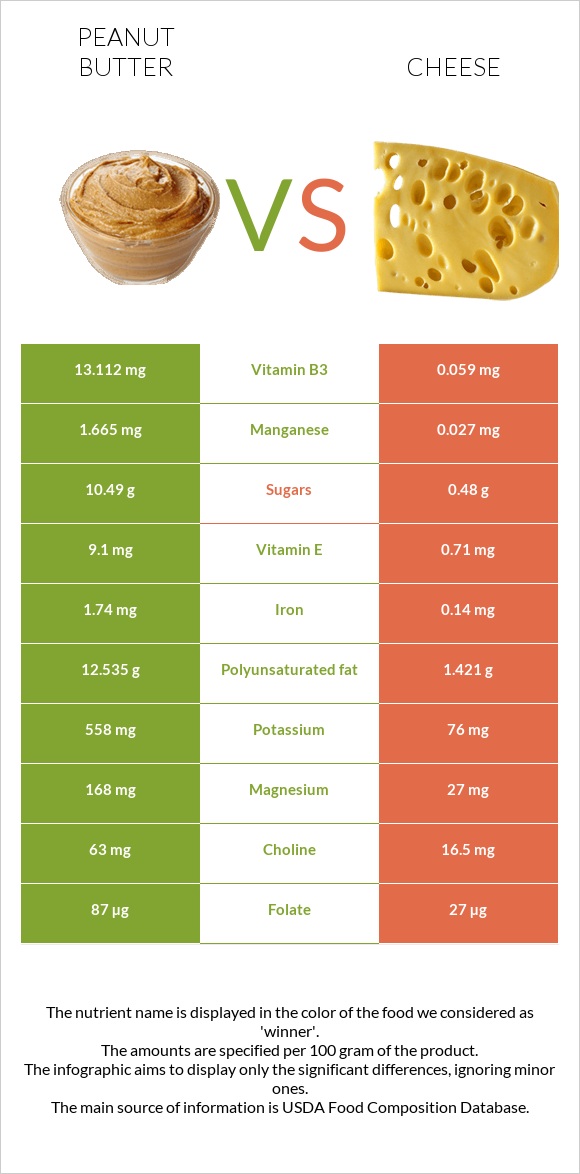
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B3 | 13.112mg | 0.059mg | 82% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 12.535g | 1.421g | 74% |
| Manganese | 1.665mg | 0.027mg | 71% |
| Calcium | 49mg | 710mg | 66% |
| Vitamin E | 9.1mg | 0.71mg | 56% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 1.1µg | 46% |
| Copper | 0.422mg | 0.03mg | 44% |
| Selenium | 4.1µg | 28.5µg | 44% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 25.941g | 9.246g | 42% |
| Saturated fat | 10.325g | 18.867g | 39% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 330µg | 37% |
| Magnesium | 168mg | 27mg | 34% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 99mg | 33% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.441mg | 0.066mg | 29% |
| Fats | 51.36g | 33.31g | 28% |
| Sodium | 17mg | 653mg | 28% |
| Iron | 1.74mg | 0.14mg | 20% |
| Fiber | 5g | 0g | 20% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.192mg | 0.428mg | 18% |
| Phosphorus | 335mg | 455mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.137mg | 0.41mg | 15% |
| Folate | 87µg | 27µg | 15% |
| Potassium | 558mg | 76mg | 14% |
| Calories | 598kcal | 404kcal | 10% |
| Zinc | 2.51mg | 3.64mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.15mg | 0.029mg | 10% |
| Choline | 63mg | 16.5mg | 8% |
| Carbs | 22.31g | 3.09g | 6% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 24 IU | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.6µg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 2.4µg | 2% |
| Protein | 22.21g | 22.87g | 1% |
| Starch | 3.56g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 17.31g | 3.09g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.49g | 0.48g | N/A |
| Trans fat | 0.075g | 0.917g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.231mg | 0.547mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.525mg | 1.044mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.616mg | 1.206mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.546mg | 1.939mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.681mg | 1.025mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.265mg | 0.547mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.202mg | 1.074mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.782mg | 1.404mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.557mg | 0.547mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.12g | 0g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.027g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.017g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.01g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.008g | 0.007g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 12.215g | N/A |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +∞% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +∞% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +100% |
| Contains more LactoseLactose | +∞% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Peanut butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172470/nutrients
- Cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173414/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





