Pork belly vs. Pork jowl — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Pork jowl is a fattier cut with higher amounts of fats and calories. In comparison, pork belly is richer in proteins and has fewer calories. Pork belly is richer in selenium, zinc, phosphorus, and vitamin B6.
In accordance, in high amounts, both negatively impact overall health.
Introduction
Pork jowl and pork belly are different cuts of pork. A pork jowl is a cut that comes from the head of the pork. On the other hand, pork belly comes from the belly of the pork. Both these cuts have different compositions regarding the meat and fat contents. Understanding the difference between these cuts is essential.
It is also important to answer whether pork meat is red or white. You can read this article to answer your question.
This article will compare these pork cuts regarding general differences, their nutrition content, and health impacts.
General differences
Pork jowl and belly are fatty cuts of pork. However, pork jowl has thick layers of fat. As an example, guanciale is a common use of pork jowl. As an example of pork belly, bacon is one of the main usages for pork belly.
They are both used in the culinary world as strips or cubes crisped up to be used in different foods.
The meat on a pork jowl is a slice of thick and chewier meat. Pork belly and jowl are mainly smoked and slowly cooked since they are not as tender as other cuts.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of each cut in raw form.
Calories
Pork jowl is higher in calories. There are 655 calories in 100g of pork jowl compared to pork belly, which contains 518 calories.
Pork jowl is on the list of top 30 foods high in calories.
Proteins
Pork belly is richer in proteins compared to pork jowl. Pork jowl contains 6.4g of protein compared to pork belly, which contains 9.3g of protein.
Fats
The fat composition of these cuts is one of the essential components.
Pork jowl contains 70g of fat compared to pork belly, which contains 53g of fat. Pork jowl is higher in fats by a very significant amount.
Pork jowl is higher in saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and cholesterol.
The saturated fat composition of pork jowl is 25g, whereas, in pork belly, the saturated fat composition is lower than 19g.
Concerning the fat content, both these cuts are highly fatty. Another comparative text is between pork shoulder vs. pork belly, which compares a less fatty cut of pork which is the shoulder.
Carbs
The carbohydrate content is negligible in both of them.
Minerals
Pork belly is richer in selenium, zinc, and phosphorus.
Below we can see the mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+33.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+25%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+25%
Contains
more
IronIron
+23.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+30%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+21.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+25.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+20%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+433.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-21.9%
Vitamins
Their vitamin content is nearly similar. They are both nearly equally rich in vitamins B1, B2, B3, and B12. Comparatively, pork belly is richer in vitamin B6.
Below we can see the vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+34.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+44.4%
Health impacts
Since pork meat is red meat, it is essential to know how red meat can impact our health. This article explains in-depth how red meat can affect your health.
Cardiovascular health
High saturated fat intake, in this case with pork jowl and pork belly, is linked with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. (1) (2)
Diabetes and metabolic diseases
Since both these foods are high in calories, unregulated consumption of high-caloric foods over a long period increases the risks of obesity and overall metabolic diseases. One of the main increased risks is type 2 diabetes, although none of these foods has a glycemic index. (3)
Infographic
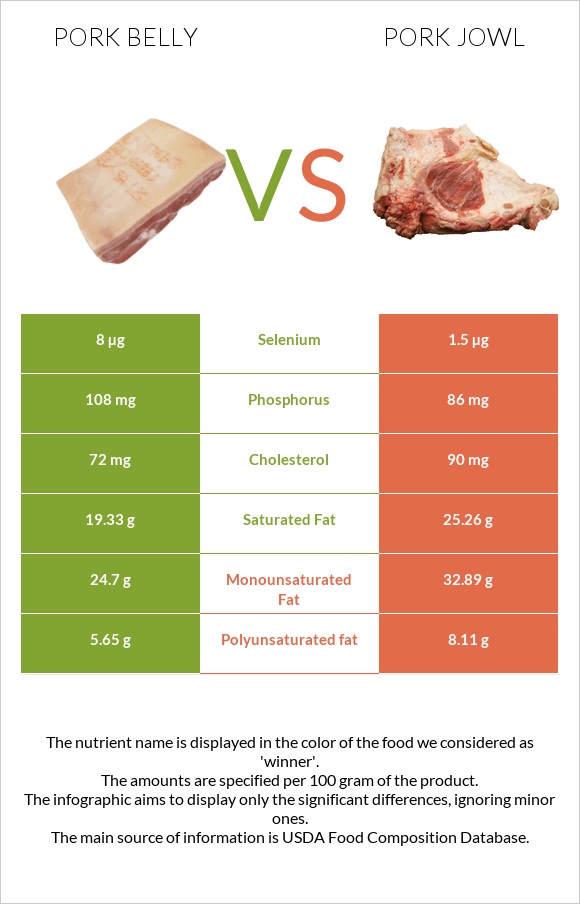
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 19.33g | 25.26g | 27% |
| Fats | 53.01g | 69.61g | 26% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 24.7g | 32.89g | 20% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 5.65g | 8.11g | 16% |
| Selenium | 8µg | 1.5µg | 12% |
| Calories | 518kcal | 655kcal | 7% |
| Protein | 9.34g | 6.38g | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 72mg | 90mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 108mg | 86mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.13mg | 0.09mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 1.02mg | 0.84mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 185mg | 148mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.52mg | 0.42mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.052mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 0.29mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.396mg | 0.386mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.647mg | 4.535mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.84µg | 0.82µg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.3mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Magnesium | 4mg | 3mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 4mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 32mg | 25mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.006mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.242mg | 0.236mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.256mg | 0.25mg | 0% |
| Folate | 1µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.21mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.168mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.446mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.528mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.095mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.239mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.305mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.072mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +46.4% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +65.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +31.3% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +100% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -23.5% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +33.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +43.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pork belly - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167812/nutrients
- Pork jowl - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168269/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.