Rice vs. Pasta — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In short, pasta is a better source of protein, vitamins, and minerals. It contains 12 times more vitamin B2 and more vitamins B1, B12, and B9 or folate, vitamin A, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and zinc.
Rice is higher in carbohydrates, such as net carbs, and consequently has higher insulin and glycemic index values. Thus, pasta may be a better choice for people with diabetes.
On the other hand, rice is 3 times richer in vitamin B6 and higher in vitamins B5, B3, calcium, and potassium. Rice is almost 2 times lower in sodium.
Introduction
A staple food in many countries, pasta, and white rice are the principal sources of carbs in various diets. This article will compare rice and pasta to see their similarities and differences, focusing primarily on nutrition and health impact.
Taste and Use
Pasta is usually made from wheat flour and water and has a slightly nutty, earthy flavor. It has a slightly chewy texture that can vary depending on the type of pasta. On the other hand, rice is a refined grain with a mild, somewhat neutral flavor that allows it to be paired with a wide variety of seasonings and side dishes.
Pasta is often used in Italian cuisine and is typically served with various sauces such as tomato sauce, pesto, or creamy sauces. It can be served as a side dish in soups, stews, and curries or as a filling in dishes like sushi or stuffed peppers. It can also be baked into casseroles or fill dishes like lasagna or cannelloni. On the other hand, rice is a staple in many cuisines, including Asian, Indian, and Latin American.
Nutrition
The nutritional information presented in this article and infographics is for 100g servings of cooked, enriched, regular, long-grain white rice and plain pasta.
The average serving size of pasta per person is 2 ounces or 128g, while this serving size for rice is a little larger - one cup weighing 158g.
Macronutrients and Calories
Cooked pasta and rice have very similar macronutrient compositions, consisting of 68-69% water and 31-32% nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+13%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+35.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+91.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+275%
Calories
The same serving size of pasta and rice provides roughly the same number of calories - 130kcal. However, rice has a slightly larger average serving size per person.
To be precise, one average serving of pasta contains 168 calories, while one serving size of rice has 205 calories.
Carbohydrates
Rice is higher in carbohydrates by about 3g per every 100g serving. The same 100g serving of pasta and rice contains 25g and 28g of carbohydrates, respectively.
Rice is also consequently higher in net carbs, as these two dishes are low in dietary fiber.
Most of the net carbs for both foods are made up of starch.
Protein
While these foods are not excellent sources of protein, pasta contains 2 times more protein than rice.
Unsurprisingly, pasta is richer in all essential amino acids than rice.
Fats
Rice contains an insignificant amount of fats, and pasta provides only 1g per 100g serving. Most of these fats are polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-48.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+40.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+464.5%
Naturally, pasta and rice do not contain cholesterol.
Vitamins
Pasta and rice are both good sources of B-group vitamins; however, pasta is richer in most of these. Pasta contains 12 times more vitamin B2 and overall more vitamin B1 and vitamin B9 or folate. Pasta also provides some levels of vitamin A and vitamin B12, which are completely absent in rice.
Nevertheless, rice is 3 times richer in vitamin B6 and nearly 2 times richer in vitamins B5 and B3.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+48.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+113.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+173.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+28.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+1053.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+10.3%
Minerals
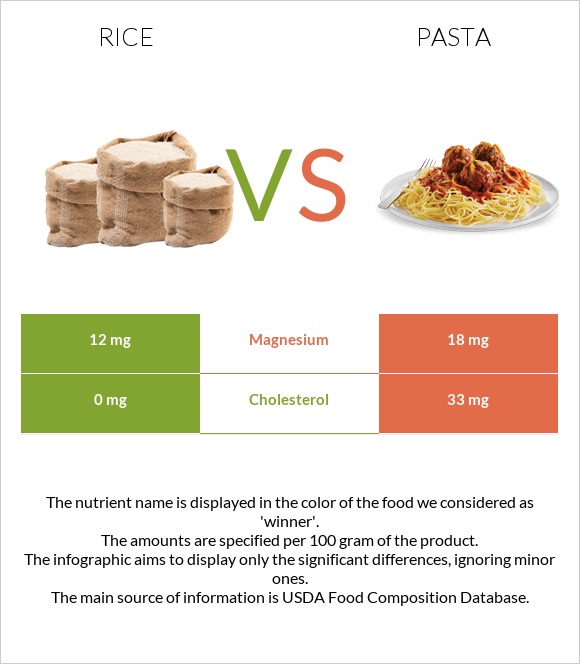
Pasta is also overall higher in minerals. Pasta provides more magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and zinc.
On the other hand, rice contains higher calcium and potassium levels. Rice is also almost 2 times lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+66.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+45.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-83.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+110.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+50%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+34.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+14.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+46.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of food differs depending on the variety and cooking method.
The average glycemic index of 9 different penne pasta varieties is 52. Fusilli pasta, made from wheat, has an average glycemic index of 58. Boiled white spaghetti has a mean glycemic index of 47. At the same time, barley pasta has a glycemic index of 62 (1).
The average glycemic index for white basmati rice is 60, which is moderate. Brown rice, on the other hand, has a low glycemic index of 50, while Jasmine white rice has a high glycemic index of 89 (1).
Insulin Index
The insulin index is another way of showing the body’s reaction to the consumption of a given food.
Pasta has been researched to have an insulin index of 29 to 40 (2, 3). On the other hand, Rice has a higher insulin index of 79 (2).
Basmati and Jasmine's white rice have also been studied to have insulin index values of 57 and 76, respectively (4).
In short, pasta tends to have lower glycemic and insulin index values than rice.
Weight Loss & Diets
Overall, pasta and rice are good options for a low-fat diet. These are not the best foods on low-calorie, low-carb, and keto diets.
Unlike wheat pasta, rice can be used on gluten-free diets. However, there are also gluten-free pasta varieties.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Eating pasta meals has been researched to be associated with a considerably lower risk of stroke and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (5).
A significant relationship between the consumption of white rice and risk factors for cardiovascular disease has been discovered by specific studies. Yet, these findings about the association between the consumption of refined rice and cardiovascular mortality were contradictory in others (6).
Diabetes
In terms of glycemic and insulin index values, pasta is a preferable choice for people with diabetes, having lower values for both.
Consuming pasta in moderation—within limits advised for total carbohydrate intake—was not linked to worsened glucose control, obesity, or other significant cardiovascular risk factors in adults with type-2 diabetes (7).
Eating a lot of white rice regularly may raise your risk of type 2 diabetes (8). For those attempting to lower their risk, limiting the intake of white rice while increasing the intake of whole grains, vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts is advised (9).
Sources.
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/66/5/1264/4655967
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25789978/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8258098/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4530655/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/1/101
- https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/43/11/2643
- https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/diacare/43/11/2625.full.pdf
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 7.5µg | 14% | |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 33mg | 11% |
| Manganese | 0.472mg | 0.224mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.013mg | 0.15mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.14µg | 6% |
| Protein | 2.69g | 5.15g | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.093mg | 0.034mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.163mg | 0.209mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.39mg | 0.183mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.069mg | 0.093mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 43mg | 63mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.476mg | 0.992mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 0.4g | 2% | |
| Folate | 58µg | 64µg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.076g | 0.429g | 2% |
| Fats | 0.28g | 1.05g | 1% |
| Carbs | 28.17g | 24.93g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 12mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Iron | 1.2mg | 1.14mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.49mg | 0.56mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 6µg | 1% |
| Calories | 130kcal | 131kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 27.77g | 24.93g | N/A |
| Calcium | 10mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 24mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.05g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 1mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.04mg | 0% | |
| Choline | 2.1mg | 0% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.077g | 0.15g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.088g | 0.124g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.031mg | 0.065mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.096mg | 0.134mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.116mg | 0.197mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.222mg | 0.348mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.097mg | 0.097mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.063mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.144mg | 0.247mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.164mg | 0.217mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.063mg | 0.103mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Rice - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168878/nutrients
- Pasta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169728/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






