Rice vs. Rice noodles — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
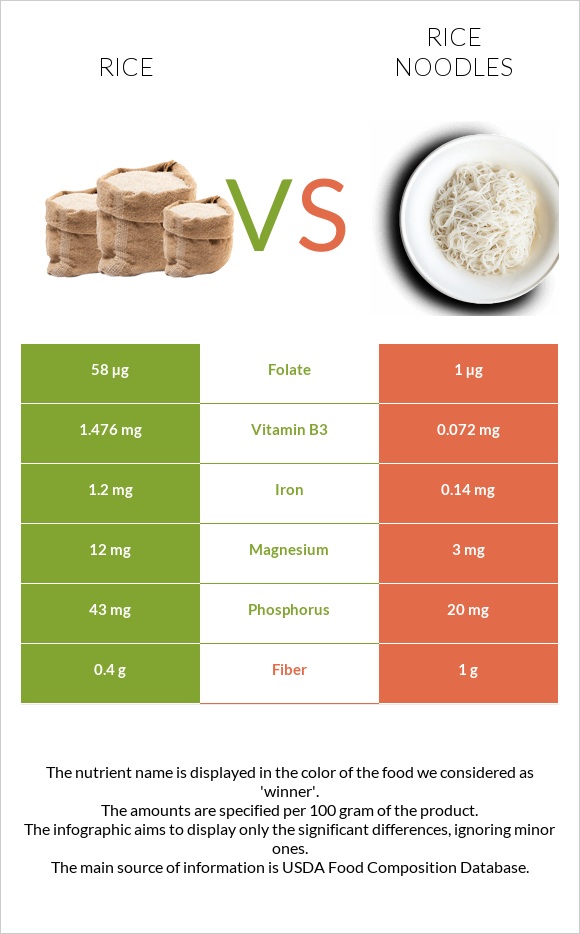
Rice noodles are one of the processed versions of rice, having a lower density of nutrients. Rice is higher in carbs and proteins, minerals, and vitamins. Rice is 58 times higher in folate. Rice provides 16% more of the DV of manganese.
Introduction
In this article, we will compare white rice and rice noodles in terms of nutrient content and health impact (1, 2). Go through all the sections of the article to find out which of these foods is a healthier choice for you.
Actual differences
Rice is an edible starchy cereal grain produced by a grass plant called Oryza sativa. It has a unique nutty but also buttery taste, which leaves a sweet aftertaste. Rice has a lot of varieties: basmati, jasmine, wild, brown, black rice, etc. Rice is usually cooked using one of these preparation methods: boiling, steaming, and making risotto or pilaf.
Rice noodles are made of rice flour and water primarily. They have a slightly sweet and nutty taste and are used for making soups, stir-fries dishes, pad Thai, sometimes pasta, and even sweet puddings.
Because rice noodles are one of the processed versions of rice, they may contain lower amounts of nutrients.
Go through the nutrition section of the article to find out more about the differences between these foods.
Nutrition
Protein
Rice protein is one of the essential plant-based proteins. Rice is higher in protein than rice noodles. It provides 2.7g of protein per 100g, compared to 1.8g of rice noodles.
Fats
Both foods have less than one gram of fat per 100g. So, the fat amount of rice and rice noodles can be neglected.
Carbs
Rice contains more carbohydrates per 100g than rice noodles.
Rice provides 28.2g of carbs, while the same amount of rice noodles has 24g. Rice provides slightly more sugar. Hence, it can seem sweeter. Rice noodles are lower in net carbs.
Fiber
Fiber type in rice-based products is usually soluble. Rice noodles are higher in terms of fiber content. They provide 1g of dietary fiber per 100g compared to 0.4g in rice.
Minerals
Rice is the winner in this section.
Rice is higher in all essential minerals compared to rice noodles. It contains more than six times more iron than rice noodles.
Their sodium content is insignificant.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+300%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+150%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+775%
Contains
more
IronIron
+757.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+81.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+96%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+115%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-94.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+314%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+66.7%
Vitamins
If we look at the vitamin comparison chart shown below, we will see that rice is higher in all types of vitamins. Rice is significantly higher in B-complex vitamins.
Rice noodles are 58 times lower in folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+805.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+225%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+1950%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+3445.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1450%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+5700%
Calories
Rice and rice noodles are classified as medium-calorie foods. Rice is 22 calories higher per 100g.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index is significant for managing diabetes. Rice’s GI equals 60, and rice noodles’ GI is 61. Both are classified as foods having medium GI. For more information, check our glycemic index chart.
Acidity
Based on PRAL values, rice (1.7) and rice noodles (1.4) are acidic.
Health impact
As mentioned above, rice is higher in nutrients than rice noodles. Hence, rice consumption can be a healthier choice. However, some studies show that you should be careful while using high amounts of rice.
The American Health Association recommends whole grains, such as brown rice, over refined ones, like white rice (3). However, according to cohort studies, a high intake of white rice is not associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (4).
That said, research has shown that rice consumption correlates with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes (5).
Although we can often find rice that is fortified with vitamin A, this research indicates rich noodles fortified with vitamin A have higher benefits in vitamin A absorption (6).
Rice noodles might contain very small amounts of gluten because of the manufacturing process. Rice is gluten-free.
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168878/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168914/nutrients
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/whole-grains-refined-grains-and-dietary-fiber
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25527760/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408398.2022.2101984
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33612590/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 0.472mg | 0.114mg | 16% |
| Folate | 58µg | 1µg | 14% |
| Iron | 1.2mg | 0.14mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.163mg | 0.018mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.476mg | 0.072mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.39mg | 0.011mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.093mg | 0.006mg | 7% |
| Selenium | 7.5µg | 4.5µg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.069mg | 0.038mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 43mg | 20mg | 3% |
| Protein | 2.69g | 1.79g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 12mg | 3mg | 2% |
| Fiber | 0.4g | 1g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.49mg | 0.25mg | 2% |
| Calories | 130kcal | 108kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 28.17g | 24.01g | 1% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 4mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 35mg | 4mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 19mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.013mg | 0.004mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.28g | 0.2g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 27.77g | 23.01g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.05g | 0.03g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.04mg | 0.03mg | 0% |
| Choline | 2.1mg | 1.6mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.077g | 0.023g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.088g | 0.026g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.076g | 0.023g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.031mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.096mg | 0.063mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.116mg | 0.073mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.222mg | 0.147mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.097mg | 0.062mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.063mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.144mg | 0.095mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.164mg | 0.104mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.063mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +50.3% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +40% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +17.3% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +133.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +238.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +230.4% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -70.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Rice - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168878/nutrients
- Rice noodles - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168914/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.