Roe vs. Caviar — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Caviar is a type of roe obtained from the sturgeon fish. Although all fish eggs are called "roe," not all "roe" are classified as caviar.
Caviar contains two times more fats than roe, although roe contains slightly more cholesterol.
The predominant vitamin in both is vitamin B12, although caviar contains approximately 2 times more vitamin B12 than roe. Caviar also contains around 15 times more iron and 12 times more magnesium. Meanwhile, roe is richer in phosphorus and contains 13 times less sodium than caviar.
Introduction
Roe and caviar are pretty similar, but they also have specific differences. Today, we will discuss the main differences between roe and caviar's nutritional and health aspects.
What's the Actual Difference?
The term "caviar" refers to the salted roe obtained from sturgeon fish belonging to the Acipenseridae family, which are found in the Black and Caspian Seas.
Varieties and Use
Different types of sturgeon produce a variety of caviar, including Osetra, Beluga, Sevruga, and Siberian caviar, among others. Typically made entirely of sturgeon fish eggs, these eggs are cured and then placed in tins for aging and storage.
Roe is the term for female fish eggs, which can come from various fish, including trout, whitefish, salmon, and even carp and shellfish. The size, texture, and color of fish eggs can vary.
When serving fish eggs, it is recommended to use a wooden spoon instead of a metal one, as metal can potentially add a metallic flavor that may interfere with the delicate taste of the eggs. Caviar is a luxury food and delicacy that is very expensive.
Many people enjoy roe with creme fraiche on top of blini, toast, or a cucumber slice. Fish eggs are also used as a garnish on many restaurant dishes and are a significant component in some sushi rolls.
Nutrition
In this section, we will be comparing the nutritional compositions of cooked, mixed-species roe with black and red, granular caviar.
The serving size for both is about 1oz or 28.35 grams. To make the comparison easier, we will often refer to 100-gram servings of each.
Macronutrients and Calories
As can be observed from the macronutrient composition charts below, caviar is slightly more nutrient-dense, consisting of 48% water, while roe contains 59% water. Caviar also contains slightly more fats and carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+16.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+23.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+117.5%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+108.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+130.8%
Calories
Caviar contains slightly more calories than roe. Roe contains 204 calories per 100g, while caviar contains 264 calories per same serving.
However, a single serving of roe (28.35 grams) only contains 57.8 calories, while a single serving of caviar contains 74.8 calories.
Carbohydrates
Although both roe and caviar are low-carb foods, caviar has a relatively higher net carb content compared to roe, with 4g per 100g, while roe contains 1.92g per 100g.
Protein
Both caviar and roe are excellent sources of high-quality protein.
Caviar provides 24.6g of protein per 100g, while roe contains 28.62g of protein per 100g.
Both caviar and roe rank among the top 13% of foods in terms of their protein content, making them significant sources of protein.
Fats
Caviar has two times higher fats compared to roe.
Caviar provides 17.9g of fat per 100g, while roe contains 8.23g of fat per 100g. In terms of fat content, caviar falls within the top 18% of foods as a source of fats.
Both foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and have no trans fats.
In terms of the fat type distribution, both have similar percentages of saturated and unsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-54%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+117.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+117.5%
Cholesterol
Caviar and roe both have high levels of cholesterol, placing them in the top 5% of foods as a source of cholesterol.
Caviar contains 479mg of cholesterol per 100g, while roe contains 588mg of cholesterol per the same serving.
Vitamins
The predominant vitamin in both is vitamin B12. A single 28.35 gram serving of roe contains 3.26µg vitamin B12, while the same serving of caviar contains approximately 2 times more (5.67µg) vitamin B12.
The daily need for vitamin B12 is about 2.4µg, which means a single serving of both roe and caviar is more than enough to satisfy the daily need.
Roe and caviar are also rich in various other vitamins. Roe contains more vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, and folate, while caviar contains more vitamin A, vitamin B5, and vitamin B6.
The amount of vitamin B5 is 3 times higher in caviar than in roe.
Additionally, roe contains vitamin C, which is lacking in caviar, while caviar contains vitamin E and vitamin D, which are lacking in roe.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+45.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+53.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+1726.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+84%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+197.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+203.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+73%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+73.3%
Minerals
Although both roe and caviar contain various minerals, caviar seems to be richer in most.
Caviar contains more iron, magnesium, calcium, and selenium. Specifically, caviar contains around 15 times more iron and 12 times more magnesium.
Meanwhile, roe is richer in phosphorus and contains 13 times less sodium than caviar.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+56.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+16.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+34.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+44.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-92.2%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+1053.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+882.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1442.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+284.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+26.7%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is a rating system used for foods containing carbohydrates. Since both roe and caviar contain only very few carbohydrates, they both are considered low glycemic index foods.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of roe and caviar are 26.1 and 10.1, respectively, which means both have acidifying effects on the body.
Health Benefits
Both caviar and roe contain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals essential for your body.
Cardiovascular Health
Both roe and caviar are great sources of omega-3 fatty acids, known for their cardiovascular benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve lipid profiles, which are important for preventing atherosclerosis (1).
However, there are some factors to consider:
Sodium Content: Caviar is often heavily salted as part of the preservation process, leading to a higher sodium content compared to roe. High sodium intake is associated with hypertension and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Cholesterol Content: Both roe and caviar contain cholesterol, but the amounts may vary depending on the species of fish. Cholesterol plays a crucial role in the normal functioning of tissues, but excessive levels can lead to metabolic disorders and elevate cardiovascular risk.
Quality and Processing: The quality and processing methods of roe and caviar can vary widely, impacting their nutritional profiles. Additionally, additives or preservatives used in processing may have implications for heart health.
In summary, both roe and caviar can be part of a heart-healthy diet due to their omega-3 fatty acid content. However, individuals should be mindful of the sodium content, particularly in caviar, and aim for moderation. As with any dietary choice, it's essential to consider overall dietary patterns and health status when incorporating roe or caviar into your diet.
Joints Health
Studies on fish eggs have not been conducted on the omega-3 fatty acids found in fish eggs and other seafood. Researchers believe that omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and fish eggs may help to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Fish eggs containing omega-3 fatty acids may also be anti-inflammatory and inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (2).
Brain and Mental Health
Since omega-3 fatty acids are used to build brain and nerve cells, fish eggs rich in omega-3 fatty acids are essential for learning and memory. It has been proposed that decreasing brain inflammation can slow the mental health decline seen in Alzheimer's disease (3).
Furthermore, Omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial during the depressive phase of bipolar disorder. People who suffer from depression have lower omega-3 fatty acid levels, implying that a lack of this nutrient may be a risk factor for depression (4).
Boost Immune System
Fish eggs contain omega-3 fatty acids and selenium, which may benefit your immune system. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and restore the barrier function of your skin, intestines, and lungs, which helps to keep harmful bacteria at bay and keeps you healthy.
Caviar is high in iron, zinc, and magnesium, both of which have antioxidant properties and may help lower oxidative stress levels in the body, reduce inflammation, and boost immunity (5).
Eye Health
Omega-3 fatty acids may aid in preventing and treating a variety of eye diseases. Consuming omega-3 fatty acids, whether in foods or as a supplement, may help reduce macular degeneration and glaucoma. According to research, omega-3 fatty acids in fish eggs can help reduce your risk of developing dry eyes, and they may also help treat bothersome symptoms. Consuming omega-3 fatty acids, whether in foods or as a supplement, may help reduce macular degeneration and glaucoma.
Moreover, omega-3 fatty acids may also aid in the prevention of high eye pressure, which can lead to glaucoma (6).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Fish allergy is one of the most common food allergies, affecting one percent of the US population. A person who is allergic to fish may also be allergic to fish eggs.
When a person with a fish allergy is exposed to that fish, proteins in the fish bind to specific IgE antibodies produced by the person's immune system, activating the person's immune defenses and resulting in mild to severe reaction symptoms (7).
Adverse Effects
Fish eggs are high in cholesterol and sodium.
If you are watching your cholesterol or limiting your salt intake, you should consult with your doctor to see if you can eat them on occasion. Remember that fish eggs are high in purines, which can be problematic if you have gout.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3712371/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28816722/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7468918/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6713969/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6834330/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7230711/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27613460/
Infographic
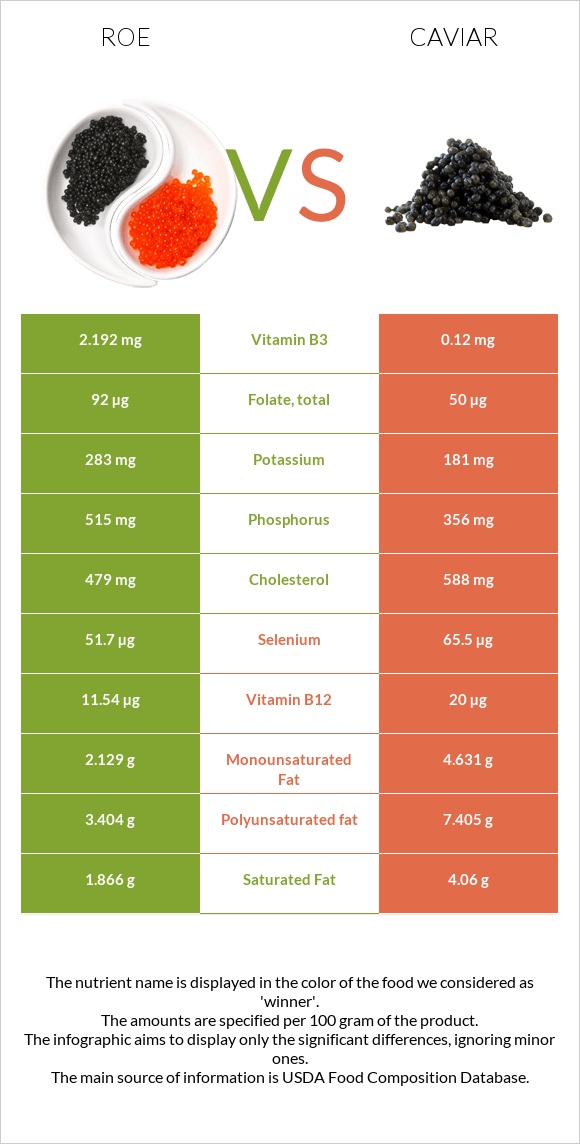
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 11.54µg | 20µg | 353% |
| Iron | 0.77mg | 11.88mg | 139% |
| Choline | 490.9mg | 89% | |
| Magnesium | 26mg | 300mg | 65% |
| Sodium | 117mg | 1500mg | 60% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.154mg | 3.5mg | 47% |
| Cholesterol | 479mg | 588mg | 36% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.404g | 7.405g | 27% |
| Calcium | 28mg | 275mg | 25% |
| Selenium | 51.7µg | 65.5µg | 25% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.949mg | 0.62mg | 25% |
| Phosphorus | 515mg | 356mg | 23% |
| Vitamin A | 91µg | 271µg | 20% |
| Vitamin C | 16.4mg | 0mg | 18% |
| Fats | 8.23g | 17.9g | 15% |
| Vitamin D | 117 IU | 15% | |
| Vitamin D | 2.9µg | 15% | |
| Vitamin E | 1.89mg | 13% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.192mg | 0.12mg | 13% |
| Folate | 92µg | 50µg | 11% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.185mg | 0.32mg | 10% |
| Saturated fat | 1.866g | 4.06g | 10% |
| Protein | 28.62g | 24.6g | 8% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.277mg | 0.19mg | 7% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.129g | 4.631g | 6% |
| Calories | 204kcal | 264kcal | 3% |
| Potassium | 283mg | 181mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 1.28mg | 0.95mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.128mg | 0.11mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.013mg | 0.05mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 1.92g | 4g | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 1.92g | 4g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.375mg | 0.323mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.305mg | 1.263mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.465mg | 1.035mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.509mg | 2.133mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.179mg | 1.834mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.71mg | 0.646mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.401mg | 1.071mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.676mg | 1.263mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.778mg | 0.649mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 1.26g | 2.741g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 1.747g | 3.8g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.105g | 0.229g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Roe - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174239/nutrients
- Caviar - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174188/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


