Wonton soup vs. Egg Drop Soup — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Wonton and egg drop soups are low-calorie soups. Wonton soup has more protein and carbs, while egg drop soup has slightly more fats.
Egg drop soup is over 5 times richer in vitamins C and A, while wonton soup is 3 times richer in vitamins B3, B6, and B12.
Both soups are high in sodium and increase the risk of certain diseases.
Introduction
This article compares two Chinese soups: wonton soup and egg drop soup.
Wonton soup is a bouillon-like soup prepared with wontons: dumplings with mainly pork or shrimp, sometimes chicken, vegetables, scallions, and various seasonings. Wonton soup is traditionally made with a clear and flavorful broth that is usually chicken or sometimes pork-based. The broth is often seasoned with garlic, ginger, and other spices.
Egg drop soup is made by dropping wispy beaten eggs into hot chicken broth. The soup may sometimes contain scallions, peppers, and tofu. Vegetable broth can also be used as a base for egg drop soup. The broth is usually lighter and less intense compared to wonton soup.
Nutrition
The nutritional values in the infographics of this article are presented for 100g servings of wonton soup and egg drop soup.
However, we will talk about the nutrition of one average serving size of wonton and egg drop soups - one cup, which is ~223g for wonton soup and ~241g for egg drop soup.
Macronutrients and Calories
Wonton and egg drop soups have similar nutritional values. However, wonton soup is slightly higher in protein and carbs, whereas egg drop soup is slightly higher in fats.
Both soups are made up of over 90% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+79.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+22.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+15%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+134.6%
Calories
Wonton and egg drop soups are low-calorie soups.
One serving of wonton soup provides 71.4 calories, whereas one serving of egg drop soup provides 65.1 calories.
Carbohydrates
One cup of wonton soup contains 11.7g of carbs, and one cup of egg drop soup contains 10.3g of carbs.
A cup of each soup provides 8-9% of the recommended daily carb intake (1).
The carbohydrate content of egg drop soup consists entirely of starch, while wonton soup also contains low levels of sucrose and maltose.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+93.9%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+∞%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Wonton and egg drop soups may or may not be considered keto-friendly, depending on the used ingredients and the soup's carb content.
Protein
The soups are not particularly rich in proteins. However, wonton soup has 1.5 times more proteins than egg drop soup.
One cup of wonton soup contains 4.64g of proteins, while one cup of egg drop soup contains 2.8g of proteins.
Fats
Wonton and egg drop soups are very low in fats.
One cup of wonton soup contains 0.58g of fats, whereas one cup of egg drop soup contains 1.47g of fats.
The soups contain trace amounts of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Wonton soup is richer in most B complex vitamins, whereas egg drop soup is richer in vitamins B2, C and insoluble vitamins A, E, and K.
Wonton soup is over 3.5 times richer in vitamins B3 and B6 and three times richer in vitamin B12.
Egg drop soup is 9.3 times richer in vitamin C and 6.8 times richer in vitamin A. One serving of egg drop soup covers 17.5% of the daily vitamin C need (1).
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+26.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+271.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+16.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+280%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+200%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+85.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+828.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+1900%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+116.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+18.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+33.3%
Minerals
Wonton soup dominates in this section; however, the difference between their mineral contents is not particularly high.
Wonton soup is richer in magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and copper. On the other hand, egg drop soup is richer in iron and calcium.
Both wonton and egg drop soups are high in sodium. One cup of each soup contains ~900mg of sodium, which is almost 40% of the daily recommended amount (1).
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+50%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+45.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+26.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+33.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+20%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+209.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+175%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+40%
Contains
more
IronIron
+23.8%
Glycemic Index
There are no calculated glycemic index values for wonton soup and egg drop soup.
Acidity
The PRAL or the potential renal acid load value measures how much acid or base is produced in the organism by the consumed food.
The PRAL value of wonton soup is -0.9, and the PRAL value of egg drop soup is -0.5, making wonton soup more acidic or more acid-producing.
Health Impact
Health Benefits
Wonton and egg drop soups are considered healthy, and depending on their ingredients, they may provide a good amount of antioxidants, minerals, and vitamins.
Wonton and egg drop soups are low-calorie foods and may be consumed during low-calorie diets. Low-calorie diets are associated with a lower risk of heart, kidney, and liver disease, better glycemic control, and reduced severity of obesity-aggravated disorders (2).
Egg drop soup is rich in vitamin C, a physiological antioxidant. Vitamin C participates in immune response, wound healing, growth and repair of tissues, and absorption of iron (3).
Wonton soup is a good vitamin B6 source. Vitamin B6 is needed for making antibodies, and hemoglobin, maintaining normal nerve function, breaking down proteins, and keeping blood sugar at normal levels (4).
Risks
Wonton and egg drop soups are high in a mineral called sodium. High sodium levels are associated with increased cardiovascular and kidney disease, osteoporosis, and cancer risks (5). Consider using low-sodium foods to avoid a high risk of heart disease.
References
- Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025
- https://jpp.krakow.pl/journal/archive/10_18/pdf/10.26402/jpp.2018.5.02.pdf
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/salt-and-sodium/
Infographic
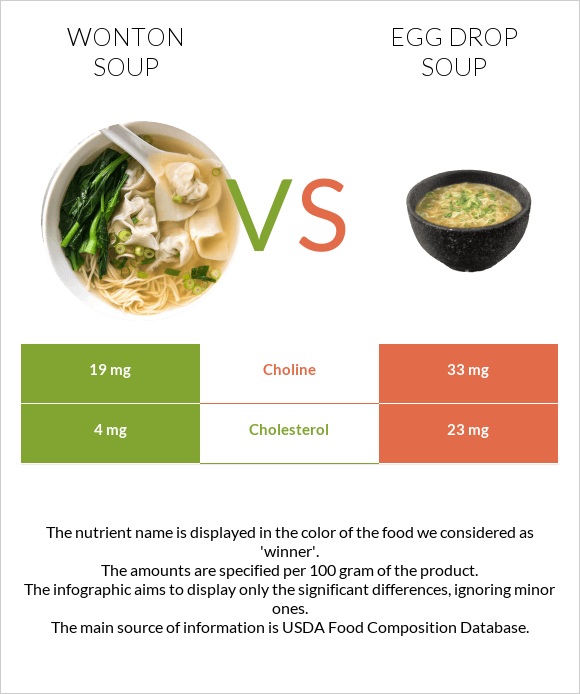
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 0.7mg | 6.5mg | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 4mg | 23mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.076mg | 0.02mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.58mg | 0.156mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.09µg | 0.03µg | 3% |
| Choline | 19mg | 33mg | 3% |
| Protein | 2.08g | 1.16g | 2% |
| Sodium | 406mg | 370mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 20µg | 2% |
| Folate | 13µg | 7µg | 2% |
| Fats | 0.26g | 0.61g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 6 IU | 1% |
| Iron | 0.21mg | 0.26mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 0.2g | 0.4g | 1% |
| Copper | 0.024mg | 0.019mg | 1% |
| Starch | 4.75g | 2.45g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.034mg | 0.011mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 1.1µg | 0.4µg | 1% |
| Calories | 32kcal | 27kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 5.05g | 3.89g | N/A |
| Carbs | 5.25g | 4.29g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 3mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 7mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 32mg | 22mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.34g | 0.09g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.12mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 18mg | 15mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.06mg | 0.13mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.024mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.016mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.14mg | 0.12mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.9µg | 1.2µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.001g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Saturated fat | 0.062g | 0.166g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.077g | 0.191g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.071g | 0.129g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.013mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.081mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.06mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.12mg | 0.047mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.062mg | 0.052mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.03mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.07mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.071mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.039mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.004g | 0.007g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.065g | 0.112g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -62.7% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +148.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +81.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Wonton soup - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171821/nutrients
- Egg Drop Soup - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174807/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


