Hoisin sauce vs. Oyster sauce — What's The Difference?


Summary
Hoisin sauce is richer in calories, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and folate. Hoisin sauce is lower in sodium than oyster sauce.
In comparison, oyster sauce contains more selenium and B12. Besides, oyster sauce is lower in carbs, including net carbs.
Introduction
In this article, we will compare two types of sauces that are frequently used in Chinese cuisine: hoisin sauce and oyster sauce.
Hoisin sauce is a dark sauce with a savory-sweet flavor. The basic ingredients are soybeans, vinegar, sugar, garlic, and chili. Hoisin sauce is frequently used with roasted Pekin duck.
In comparison, oyster sauce is derived from oysters and infused with soy sauce, sugar, and salt. It is similarly dark and brown but has a different flavor profile, blending umami, savory, and slightly sweet flavor.
Oyster sauce is used as a marination sauce and in stir-fries and dish flavoring. Oyster sauce is also frequently used in other Southeast Asian gastronomy.
Oyster sauce is not a vegan sauce. However, hoisin sauce is supposed to be vegan.
Nevertheless, more often, producers add animal-based products to them. It is essential to read the label.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare 100g of each sauce.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+145.2%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1256%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+303.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+80.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+49.9%
Calories
One of the significant differences between these two sauces is their calories. Hoisin sauce has 220 calories, and oyster sauce has 51 calories.
There are about 4.3 times more calories in hoisin sauce.
Carbs
Hoisin sauce contains 4.3 times more carbs than oyster sauce. Hoisin contains 44g of carbs. In comparison, the oyster sauce contains 11g.
Fats
Their total fat content is low, and that of oysters is negligible. However, hoisin sauce contains higher amounts of fats, but this amount doesn't have much significance.
Protein
They don't have significant amounts of protein, but hoisin sauce is slightly richer in protein.
Below are the macronutrient distributions of each sauce.
Minerals
Hoisin sauce is richer in magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. The amount of potassium in hoisin sauce is two times higher than in oyster sauce. Hoisin sauce is also lower in sodium.
On the other hand, oyster sauce is richer in selenium.
Sodium
Sodium needs a special section in this comparison because they are both very high in sodium. The health section will focus on why high amounts of sodium are dangerous.
Oyster sauce is much higher in sodium compared to hoisin sauce.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+500%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+120.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+461.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+255.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+72.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-40.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+379.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+14.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+144.4%
Vitamins
Hoisin sauce is richer in vitamins B2, and oyster sauce is richer in vitamins B3 and B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+75%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+325%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+287.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+53.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+26%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Health Impact
One of the essential health impacts that both these sauces can have is on the cardiovascular system.
They contain very high amounts of sodium, and more often, the salty flavor is obscured by other flavors. Often we overuse them, and without realizing it, we increase our sodium salt consumption.
High sodium consumption is linked with increased risks of hypertension, and in addition, hypertension increases risks of overall cardiovascular mortality rates. In this comparison, the oyster sauce contains much higher amounts of sodium than hoisin and poses a higher risk. (1)(2)
Infographic
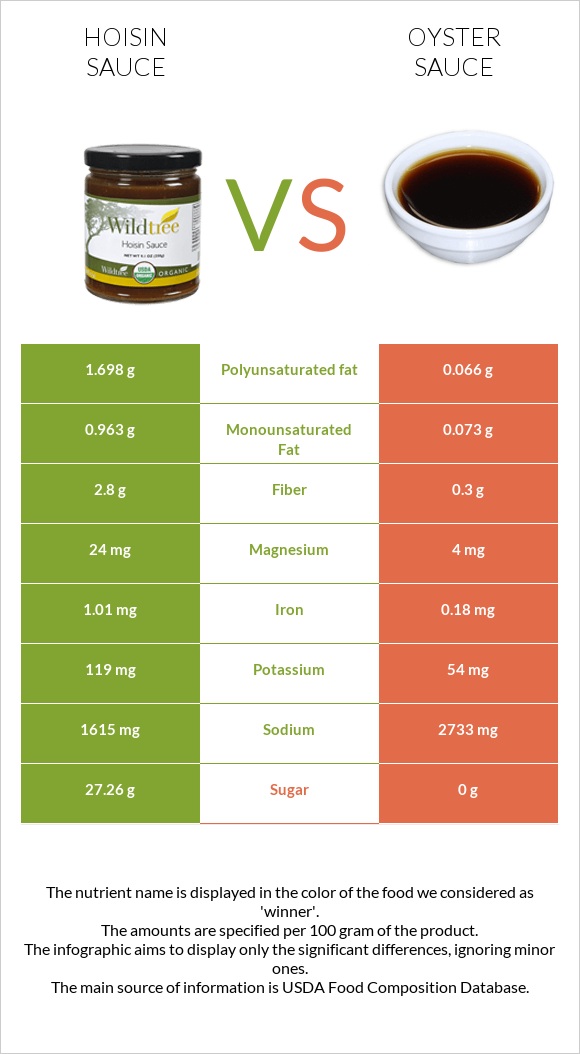
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Sodium | 1615mg | 2733mg | 49% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.41µg | 17% |
| Carbs | 44.08g | 10.92g | 11% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.698g | 0.066g | 11% |
| Iron | 1.01mg | 0.18mg | 10% |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 0.3g | 10% |
| Manganese | 0.254mg | 0.053mg | 9% |
| Calories | 220kcal | 51kcal | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.217mg | 0.124mg | 7% |
| Fats | 3.39g | 0.25g | 5% |
| Magnesium | 24mg | 4mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 1.8µg | 4.4µg | 5% |
| Protein | 3.31g | 1.35g | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.062mg | 0.016mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 119mg | 54mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.128mg | 0.147mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.32mg | 0.09mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 38mg | 22mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.28mg | 0mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.17mg | 1.474mg | 2% |
| Folate | 23µg | 15µg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 0.568g | 0.043g | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.963g | 0.073g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 3mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.004mg | 0.01mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.068mg | 0.016mg | 1% |
| Choline | 8mg | 3.5mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.4mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 41.28g | 10.62g | N/A |
| Calcium | 32mg | 32mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 27.26g | 0g | N/A |
| Vitamin K | 0.5µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1219.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +2472.7% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -92.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Hoisin sauce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172886/nutrients
- Oyster sauce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174529/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





