Pudding vs. Custard — What Is The Difference?


Summary
Chocolate pudding contains more phosphorus and iron, while custard is richer in vitamins B2, B5, and B12. 100g of pudding covers 102% of the DV of phosphorus. Custard is nine times higher in cholesterol and three times lower in sodium.
Introduction
A cooked mixture of milk or cream, butter, sugar, and flour is called pudding. Pudding can be made without eggs, with the thickness coming from cornstarch or flour. This creamy dish is best served in a bowl, occasionally with berries or whipped cream on top. Chocolate pudding contains chocolate or cocoa powder additionally. This dessert is trendy in America and the United Kingdom.
Custard is a cooked combination of eggs, cream, and sweetened milk. It serves as the foundation for a variety of sweets, including pastry cream, crème brûlée, crème caramel, and crème anglaise. Eggs are a key custard ingredient since they are a thickening agent. The custard thickens as the egg yolk-to-cream ratio increases.
Actual Differences
While both have many similarities, pudding, and custard are different, especially regarding ingredients and preparation. Let us go through some differences between these two.
The main difference between pudding and custard is the thickening agent used for the preparation of each dessert. Pudding uses cornstarch or flour as a natural thickening agent instead of eggs to transform sweetened milk into your favorite dessert. Eggs are a necessary custard ingredient since they give the dessert gelatinous consistency.
Pudding is lighter and fluffier than traditional custard. Custard has a heavier and firmer texture.
One of the key differences is flavoring. Everyone knows about pudding's chocolate and vanilla flavors, but usually, no one flavors custard.
Nutrition
Now let's explore the nutritional differences between chocolate pudding and egg custard. Both desserts contain nearly 75% of water but differ in the distribution of other nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+11.6%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+26.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+27%
Calories
Both pudding and custard are medium-calorie food products. Custard is higher in calories: it provides 122 calories per 100g, while the same amount of pudding has 105 calories.
Fats
There is a significant difference between the fat content of these two desserts: custard pastry has 2.1g more fat. Custard is higher in saturated fats.
Cholesterol
Custard is nearly nine times richer in cholesterol. Pudding provides 6mg of it, while custard contains 51mg.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-10.9%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+37.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+73.3%
Carbs
The amounts of carbs in the two desserts come from their ingredients. Pudding is a little higher in carbs than custard: 100g contains 18.9g and 17.6g of carbohydrates. Custard is higher in sugar content. Pudding provides more dietary fiber than custard.
@carbcontent
Protein
Custard and pudding contain some proteins due to their ingredients. Custard contains 0.84 more protein per 100g, so that this difference can be neglected.
Minerals
The mineral composition of these food products is almost similar. However, pudding is higher in iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and copper. In contrast, calcium, potassium, and zinc levels are higher in custard. Check the mineral comparison in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+25%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+270%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+1285.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+31.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+38%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+49.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-14.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+62.2%
Vitamins
Custard has higher vitamin content than pudding. Custard is richer in all B-complex vitamins. Pudding is eight times richer in vitamin C. Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+60.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+40.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+114.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+113.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+67.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+125%
Glycemic index
Both custard and pudding are considered to have a low glycemic index. However, pudding's GI (51) is higher than the GI of custard (35). You can check the GI values for the other foods by visiting our glycemic index chart.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of custard is lower than that of pudding. Custard has an insulin index of 57, whereas the insulin index of the pudding is equal to 80.
Infographic
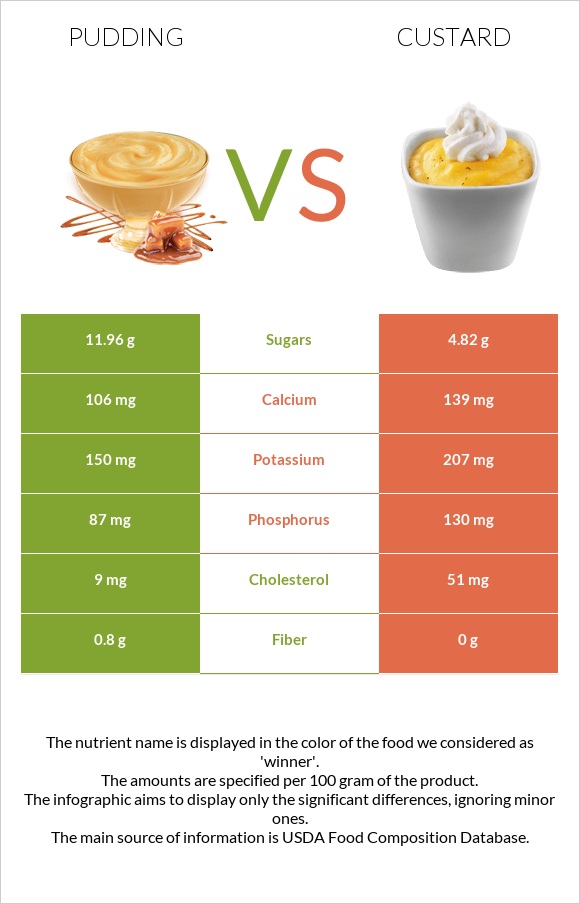
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Cholesterol | 9mg | 51mg | 14% |
| Copper | 0.111mg | 0.03mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.31µg | 0.52µg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.326mg | 0.699mg | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 87mg | 130mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.157mg | 0.22mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.097mg | 0.007mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 3.7µg | 6µg | 4% |
| Calcium | 106mg | 139mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 0.8g | 0g | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.03mg | 0.064mg | 3% |
| Protein | 3.16g | 3.99g | 2% |
| Potassium | 150mg | 207mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.038mg | 0.061mg | 2% |
| Fats | 3.15g | 4g | 1% |
| Carbs | 19.64g | 17.6g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 20mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 98mg | 84mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 39µg | 52µg | 1% |
| Folate | 4µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 1.81g | 2.032g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.819g | 1.127g | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.18g | 0.312g | 1% |
| Caffeine | 2mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Calories | 120kcal | 122kcal | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 18.84g | 17.6g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 44 IU | 47 IU | 0% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.34mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 11.96g | 4.82g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.48mg | 0.51mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.06mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 1.1µg | 1.2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.133mg | 0.132mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 0.2µg | 0% |
| Choline | 11.3mg | 11.8mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.082mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.192mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.207mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.337mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.214mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.091mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.173mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.233mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.092mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pudding - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169604/nutrients
- Custard - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168773/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




