Salami vs. Summer Sausage — Nutrition Comparison and Health Impact


Summary
Salami is more nutrient dense than summer sausage and richer in minerals like copper, zinc, phosphorus, manganese, and selenium. Salami has richer B complex vitamins and is richer in proteins. In comparison, summer sausage is richer in vitamin B12, iron, higher in saturated fats, and lower in sodium.
Introduction
This text compares two types of processed meats that are different types of sausages; salami and summer sausage.
Summer sausage is also known as cervelat.
The name summer sausage comes from the tradition of being prepared in the summer; since summer days are dried and warmer, summer sausage is dried and smoked optimally to give its specific taste and texture, which we will discuss in the following sections.
In this article, we will compare salami and summer sausage to one another according to their general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
The general differences between these 2 sausages come from their taste, usage, and preparation methods.
Taste
The main difference that will affect the taste is the fermentation process.
Salami is a fermented and then dried-up sausage, whereas summer sausage is usually cooked at lower temperatures and dried up.
This fermentation process will give salami a stronger and more robust flavor than summer sausage.
Salami and summer sausage are usually prepared in common recipes by mixing pork and beef.
Overall, salami has a more robust and stronger flavor than summer sausage. Summer sausage, in comparison, has a milder, savory-sweet taste.
Usage
These can be used in various forms; they can be used as they are with crackers, and they can be used in sandwiches. The most common usage of salami is wine and cheese and as a topping on a diavola pizza, which gives it an extra spicy taste.
Preparation methods
As mentioned above, both use a pork and beef mixture. However, summer sausage can contain game meat such as venison meat.
Salami undergoes an additional fermentation process before it dries up. In comparison, summer sausage doesn’t have this fermentation step during its preparation.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g of each.
Calories
Summer sausage contains slightly higher amounts of calories.
Protein
Salami is richer in proteins compared to summer sausage. Salami contains nearly 22g of protein, and summer sausage contains about 17g of protein.
Carbs
Their carb content is negligible.
Fats
Both are considered high-fat sausages. In comparison summer sausage is higher in fats compared to salami.
It is important to mention that summer sausage is higher in saturated fats than salami.
Minerals
Salami is mineral dense and richer in minerals compared to summer sausage. However, there is a concern which is the amount of sodium.
Salami is richer in selenium, manganese, copper, zinc, and phosphorus. In comparison, summer sausage is richer in iron.
Salami is higher in sodium compared to summer sausage. Noting that eating 100g of salami is nearly the amount of the daily sodium allowance.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+46.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+53.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+410%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+30.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+2956.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+317.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+440%
Contains
more
IronIron
+44.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-14.8%
Vitamins
Salami has a richer and dense vitamin profile compared to summer sausage. Salami is richer in all B complex vitamins except vitamin B12 which is higher in summer sausage. Summer sausage is also richer in vitamins C and D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+233.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+47.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+123.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+108.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+58%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+253.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+13.8%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+133.3%
Health impacts
In this section, we will compare the health impacts of each food, considering the negative and positive health impacts.
Impact on the gut health
Since salami is fermented, it contains healthy probiotics for our gastrointestinal system. However, we should mention that they contain nitrites, nitrates, and high sodium. However, these probiotics make it to our gastrointestinal system and give us benefits.
Also, we should ensure that a better option for salami is one with the natural casing of the meat and not synthetic ones (1)(2).
However, salami contains nitrosamines that cause negative health impacts, such as increased risks of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer (3).
The same nitrogen compounds are present in summer sausage aswell and are associated with negative health impacts. However, since summer sausage is not fermented, it does not contain probiotics (4).
Cardiovascular health
Summer sausage contains higher amounts of fats and saturated fats, which are associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis (5).
In comparison, salami is higher in sodium which increases the risks of hypertension and overall is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular mortality (6).
Miscellaneous
Salami is more nutrient dense regarding proteins, minerals, and vitamins. It can be considered as a better alternative because of all these attributes.
Infographic
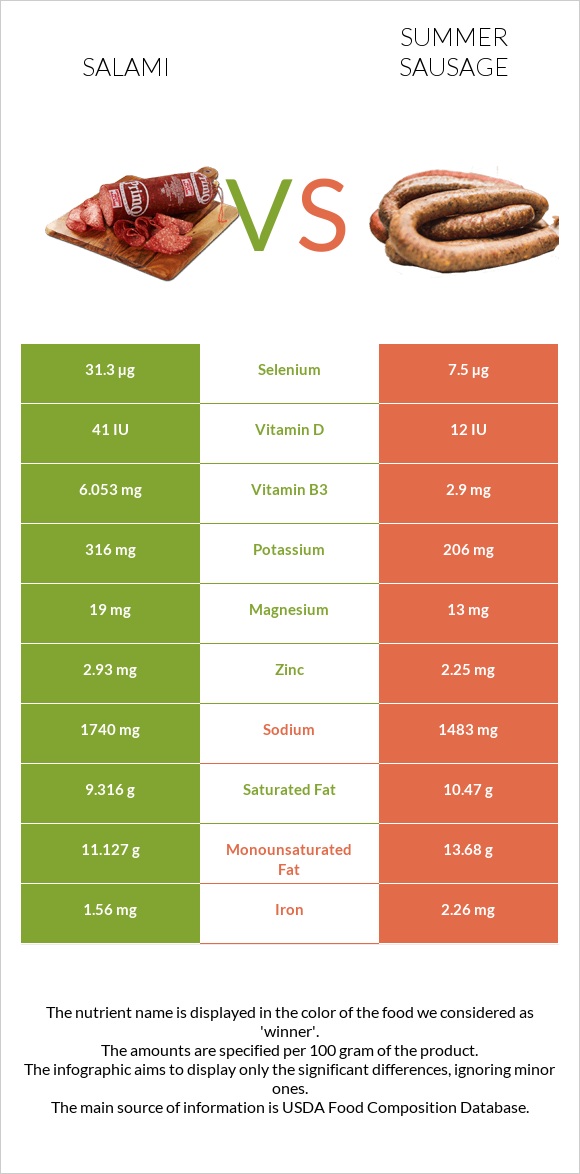
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 31.3µg | 7.5µg | 43% |
| Manganese | 0.978mg | 0.032mg | 41% |
| Copper | 0.357mg | 0.07mg | 32% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 225µg | 25% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.459mg | 0.13mg | 25% |
| Vitamin B3 | 6.053mg | 2.9mg | 20% |
| Fats | 25.9g | 37.91g | 18% |
| Choline | 93.5mg | 17% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.357mg | 0.16mg | 15% |
| Sodium | 1740mg | 1483mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.367mg | 0.249mg | 10% |
| Iron | 1.56mg | 2.26mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.201mg | 0.76mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.52µg | 1.73µg | 9% |
| Calcium | 15mg | 81mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 2.93mg | 2.25mg | 6% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 11.127g | 13.68g | 6% |
| Calories | 336kcal | 426kcal | 5% |
| Protein | 21.85g | 19.43g | 5% |
| Saturated fat | 9.316g | 10.47g | 5% |
| Vitamin D | 41 IU | 12 IU | 4% |
| Vitamin D | 1µg | 0.3µg | 4% |
| Potassium | 316mg | 206mg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 3.2µg | 3% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.529g | 3.02g | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 191mg | 178mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 19mg | 13mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 0g | 0.2g | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.22mg | 1% | |
| Folate | 3µg | 7µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 2.4g | 1.62g | N/A |
| Carbs | 2.4g | 1.82g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 89mg | 89mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.96g | 0.12g | N/A |
| Trans fat | 0.586g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.114mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.521mg | 0.54mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.675mg | 0.62mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.929mg | 1.1mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.107mg | 1.16mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.301mg | 0.36mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.481mg | 0.56mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.668mg | 0.69mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.359mg | 0.47mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.126g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.084g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.104g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +12.5% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +31.9% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +24.8% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +46.4% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -11% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +22.9% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +19.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salami - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172936/nutrients
- Summer sausage - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174599/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






