Dried Tarragon vs. Dried Thyme - Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison


Summary
While thyme is higher in carbohydrates, containing 5 times more dietary fiber, tarragon is 1.6 times higher in net carbs. Thyme is also somewhat higher in calories, while tarragon contains more protein.
Tarragon is a better source of vitamins, providing 4 times more vitamin B6 and 3 times more vitamin B2. That being said, thyme is the winner in the mineral category, being richer in calcium, zinc, and copper.
Introduction
Although both are spices with distinct aromas, tarragon and thyme have a lot of differences in terms of the nutrients they provide. This article will compare the nutritional values and health impacts of dried tarragon and thyme (1, 2).
Taste and Use
Tarragon has a delicate flavor with hints of anise or licorice. It is slightly sweet with a mild bitterness. Thyme has a more robust and earthy flavor with subtle floral and minty notes. It is less sweet and more pungent compared to tarragon.
Tarragon has a pleasant, aromatic scent, often described as a mix of anise and vanilla. Thyme has a strong, herbaceous aroma, which can vary slightly depending on the specific thyme variety.
Tarragon is commonly used in French cuisine and pairs well with chicken, fish, and egg dishes. It is a key ingredient in sauces like Béarnaise and tartare sauce. Tarragon is also a component of the classic herb blend "Fines Herbes."
Thyme is widely used in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines. It complements various meats, roasted vegetables, and tomato-based dishes. It is often included in spice blends like Herbes de Provence and Za'atar. Thyme is excellent for adding depth to hearty and savory dishes. It stands up well to longer cooking times and is perfect for stews, soups, and roasted meats.
Nutrition
The nutritional infographics below are presented for 100g servings of dried thyme and tarragon. However, these spices are naturally not used in such large quantities at once. One average serving of these spices per person is 1 teaspoon, equal to 0.6g for tarragon and 1g for thyme.
Macronutrients and Calories
Spices, including tarragon and thyme, are very nutrient-dense. Both are made up of 8% water and 92% nutrients.
Thyme is higher in carbohydrates, while tarragon contains more protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+149.9%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+27.3%
Calories
Tarragon is only slightly higher in calories. Overall, these spices add insignificant amounts of calories to the dish.
1g serving of tarragon provides 2.95 calories, and 1g of thyme has 2.76 calories.
Carbs
Thyme is higher in carbohydrates, containing 0.64g per 1g, while 1g of thyme provides 0.5g. Despite this, tarragon is 1.6 times higher in net carbs, whereas thyme is 5 times richer in dietary fiber.
Proteins
While these spices are not great sources of protein, tarragon is 2.5 times richer in this nutrient. 1g of tarragon and thyme contain 0.23g and 0.09g of protein, respectively.
Fats
Tarragon and thyme contain similarly low amounts of fats - nearly 0.07g per 1g serving.
Vitamins
Spices, being very dense in micronutrients, can be a good way to add more vitamins to a dish.
Tarragon is a better source of most vitamins, providing 4 times more vitamin B6 and 3 times more vitamin B2. It is also richer in vitamins B3 and A.
That being said, thyme is 2 times richer in vitamin B1.
These two spices are equally rich in vitamins A, C, and B9 or folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+235.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+81.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+338.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+104.4%
Minerals
Thyme can be considered the winner in the mineral category. It provides 4 times more iron and is richer in calcium, zinc, and copper. Thyme is also somewhat lower in sodium.
On the other hand, tarragon is 4 times richer in potassium and has more magnesium and phosphorus.
The two provide nearly equal amounts of selenium and manganese.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+57.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+271%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+55.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+65.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+282.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+27%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+58.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-11.3%
Glycemic Index
Due to the difficulty of consuming large portions of these spices, exact numbers for their glycemic index values have not yet been calculated.
However, tarragon has been studied to lower the glycemic index of the food it's used along with (3).
Health Impact
Antioxidant Effects
Thyme and tarragon are known for their strong antioxidant qualities. By helping neutralize harmful free radicals, antioxidants help prevent various cardiovascular diseases.
The antioxidant effects of these spices are mainly attributable to their abundance of phenolic and flavonoid compounds. They are connected to their capacity to function as free radical scavengers and oxidative enzyme inhibitors (4, 5).
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Thyme and its extracts have traditionally been used to treat inflammatory disorders worldwide, and numerous studies have demonstrated its anti-inflammatory qualities through various mechanisms (4).
Similarly, tarragon has been researched for its anti-inflammatory qualities and pain-killing, immunomodulatory, and antidepressant effects (6).
Antibacterial Effects
Tarragon and thyme oils have antibacterial effects against resistant strains of some bacteria that cause foodborne illness. Research shows that tarragon oil is effective against Staphylococcus aureus and E.Coli (6). Thyme oil also protects against Enterococcus and Pseudomonas bacteria (7).
Cardiovascular health
Antioxidant Content: Dried thyme has stronger antioxidants like thymol, carvacrol, and rosmarinic acid than dried tarragon. This makes thyme better at reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which helps prevent atherosclerosis, the main cause of coronary heart disease.
Blood Pressure Regulation: Both herbs help regulate blood pressure, but thyme offers added benefits because its active compounds, like thymol and carvacrol, can relax blood vessels and lower arterial blood pressure (8).
LDL Cholesterol Levels: While both herbs help lower LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels, thyme may be more effective due to its higher fiber content and the presence of rosmarinic acid (9).
Including these herbs in your diet can promote cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation and helping control blood pressure.
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170937/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170938/nutrients
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5897315/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9147557/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8076785/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22783458/
- Antibacterial Activity of Thyme and Lavender Essential Oils
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6270466/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34680102/
Infographic
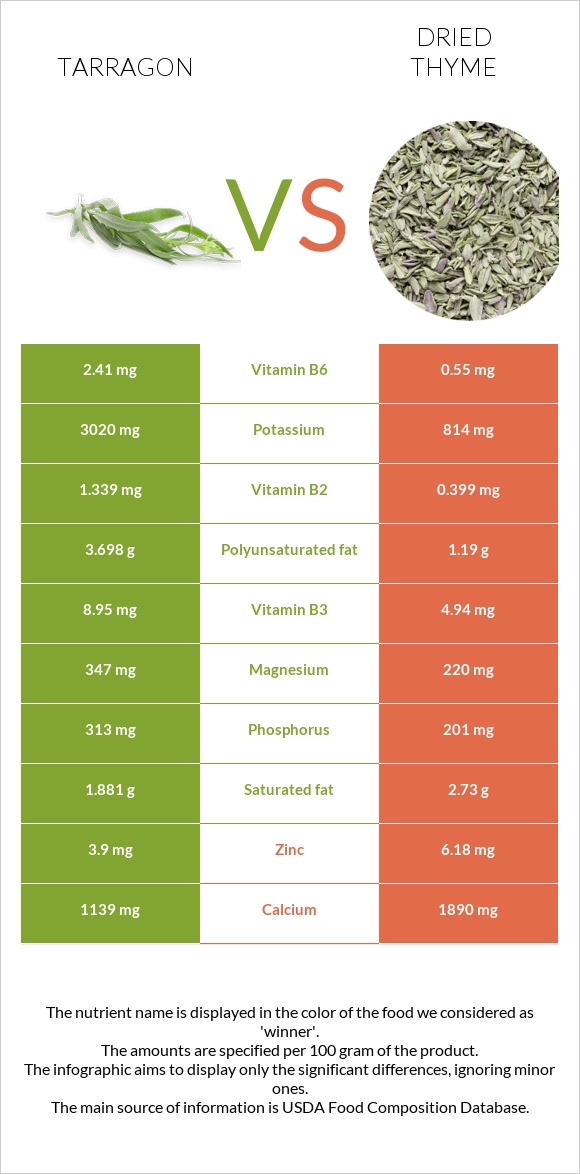
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 1714.5µg | 1429% | |
| Iron | 32.3mg | 123.6mg | 1141% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.41mg | 0.55mg | 143% |
| Fiber | 7.4g | 37g | 118% |
| Calcium | 1139mg | 1890mg | 75% |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.339mg | 0.399mg | 72% |
| Potassium | 3020mg | 814mg | 65% |
| Vitamin E | 7.48mg | 50% | |
| Magnesium | 347mg | 220mg | 30% |
| Protein | 22.77g | 9.11g | 27% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.95mg | 4.94mg | 25% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.251mg | 0.513mg | 22% |
| Zinc | 3.9mg | 6.18mg | 21% |
| Copper | 0.677mg | 0.86mg | 20% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.698g | 1.19g | 17% |
| Phosphorus | 313mg | 201mg | 16% |
| Choline | 43.6mg | 8% | |
| Carbs | 50.22g | 63.94g | 5% |
| Manganese | 7.967mg | 7.867mg | 4% |
| Saturated fat | 1.881g | 2.73g | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 210µg | 190µg | 2% |
| Calories | 295kcal | 276kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 7.24g | 7.43g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 50mg | 50mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 42.82g | 26.94g | N/A |
| Sugar | 1.71g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 62mg | 55mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 4.4µg | 4.6µg | 0% |
| Folate | 274µg | 274µg | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.474g | 0.47g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.186mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.252mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.468mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.43mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.207mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.502mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -31.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +210.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Tarragon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170937/nutrients
- Dried thyme - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170938/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.