Steak vs Ground Beef - Nutrition Comparison & Health Impact


Summary
Ground beef is lower in total fats and saturated fats. Ground beef is richer in vitamins B12 and B5. In comparison, steak is richer in zinc, selenium, monosaturated fats, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6. Ground beef has a high risk of food-borne illnesses.
Introduction
This article will compare steak and ground beef to one another according to their differences. The comparison will be between beef steak and ground beef meat.
Although we can find steak and ground meat from different animals, our comparison will be about beef.
Steak can be from different cuts, such as the ribeye, tenderloin, sirloin, t- bone, among others. Another feature of steak is the grading. A prime steak is when you have marbling in between the muscle fibers. While cooking this steak, the fat will melt and give flavor and tenderness to it.
Lower grades have less to no marbling, meaning the flavor is less, and it won't be as tender as a prime steak. This article will compare a trimmed-fat rib eye steak to 70% lean meat and 30% fat ground beef.
We will compare them based on their differences in nutritional contents and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100 g of each food in cooked forms.
Calories
Their caloric content is nearly similar. Steak has a slightly higher caloric content of 271 calories. In comparison, ground beef has 241 calories.
Carbs
Their carbohydrate content is negligible.
Fats
A ribeye steak is higher in fat compared to ground beef. It contains 19g of fat which are primarily monounsaturated fats. Ground beef contains 15.4g of fat, primarily monounsaturated fats.
It is important to note that both these foods are high in saturated fats. Comparatively, steak contains higher amounts of saturated fats, and it contains 8.4g of saturated fats, compared to ground beef which contains 6g of saturated fats.
Protein
Both are rich in protein. Steak contains 25g of protein, whereas ground beef contains 24g of protein. Their difference is not so significant.
Red meat, in this case, steak and ground beef, are a great source of protein.
This list displays foods that are categorized as foods rich in protein.
Minerals
Red meat is packed with minerals. They are a good source of iron, copper, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, and selenium. Both are rich in these minerals. However, comparatively, steak is richer in selenium and zinc. The remaining minerals are almost similar, with some negligible differences.
To better understand the mineral distribution, the diagram below displays the comparative distribution of their minerals.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+175%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+35.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+15.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-20.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+66.5%
Vitamins
Steak is richer in vitamins B2, B3, and B6. In addition, it is rich in vitamin B12. However, comparatively, ground beef is richer in vitamins B12 and B5.
The diagram below displays the comparative distribution of their vitamins
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+13.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+81.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+16.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+45.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+76%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+27.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+60.8%
Health impacts
Infections
Steak can be eaten medium or rare; ground beef shouldn't be eaten like that. Burger patties are ground beef that shouldn't be eaten medium rare. This is mainly because ground beef gets mixed in the meat grinder and exposed to all sorts of bacteria and cross contaminants. One of the primary infections that come with uncooked meat that causes diarrhea is E Coli. One of the severe outcomes of this infection would be hemolytic uremic syndrome. Thus to reduce the risks of food-borne disease, you should always eat ground meat well done. (1) (2)
Anemia
Vitamin B12 and iron are needed to produce healthy red blood cells. A deficiency in either would cause anemia. It is essential to have diets rich in these nutrients. Both are excellent sources of vitamin B12 and iron; ground beef is richer in vitamin B12. (3)
This paper aims to show that eliminating red meat from diets has adverse effects, one of which is iron deficiency anemia. (4)
Red meat allergy and intolerance
Intolerance is usually followed up after bariatric surgeries, which aim for weight loss. Several issues will arise with these surgeries, such as dumping syndrome and pancreatic juice not being exposed properly to food passing through the intestines, leading to intolerance due to indigestion.
On the other hand, allergy is a different topic related to red meat. The person cannot eat red meat in case of allergy, but in case of intolerance, a small amount could be consumed without a problem.
In detail, this article discusses the differences between red meat intolerance and allergy.
Negative impacts of red meat
Red meat has several negative impacts when eaten in high amounts, and even sometimes, moderate amounts are associated with adverse health impacts. This article discusses red meat's negative impacts on metabolic and cardiovascular health.
Infographic
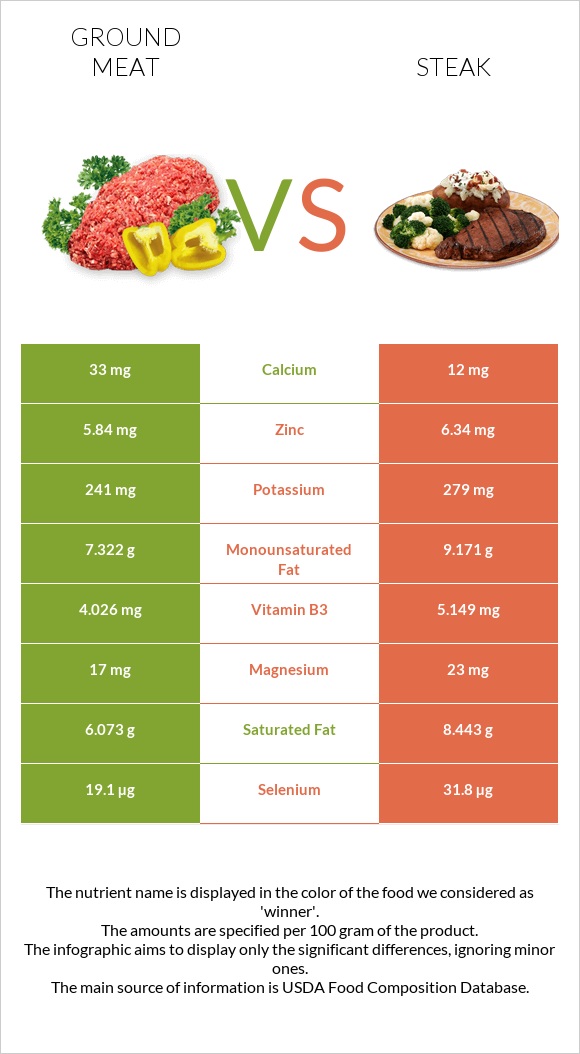
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 19.1µg | 31.8µg | 23% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.311mg | 0.5mg | 15% |
| Choline | 73.2mg | 13% | |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.49µg | 2.2µg | 12% |
| Saturated fat | 6.073g | 8.443g | 11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.171mg | 0.301mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.512mg | 10% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.026mg | 5.149mg | 7% |
| Fats | 15.37g | 19.02g | 6% |
| Zinc | 5.84mg | 6.34mg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.322g | 9.171g | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 78mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.408g | 0.896g | 3% |
| Calories | 241kcal | 271kcal | 2% |
| Protein | 23.87g | 24.85g | 2% |
| Calcium | 33mg | 12mg | 2% |
| Iron | 2.27mg | 2.4mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.051mg | 0.074mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 6 IU | 1% |
| Magnesium | 17mg | 23mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 241mg | 279mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.079mg | 0.085mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 73mg | 58mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.9µg | 1.6µg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 166mg | 163mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 7µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0% | |
| Folate | 7µg | 6µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 1.173g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.121mg | 0.278mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.923mg | 1.171mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.055mg | 1.157mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.861mg | 2.142mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.976mg | 2.38mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.614mg | 0.672mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.931mg | 0.997mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.172mg | 1.242mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.775mg | 0.931mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.013g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.008g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more OtherOther | +342.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +23.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -28.1% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +25.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +119.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground beef - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169474/nutrients
- Steak - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172164/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






